Suppose the local movie theater is offering four different movies on the next four Saturdays. And according
Question:
Suppose the local movie theater is offering four different movies on the next four Saturdays. And according to your taste in movies, each Saturday’s movie will be better than the previous week’s movie. You can go to three of the movies, but you must reserve one Saturday to see the doctor. Over the next four weeks, you will choose a Saturday to skip the theater and have your checkup. Your health insurance runs out at the end of the month, so if you haven’t seen the doctor yet by the last Saturday, you will be compelled to go then, even if the movie in the theater that afternoon is really good.
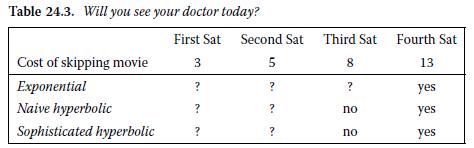
Table 24.3 lists the benefits and costs of choosing each particular Saturday, along with several partially filled rows. A “yes” indicates that you would choose to go to the doctor on that Saturday given that you have not already done so, and a “no” indicates you would not. To make your decision each Saturday, you compare your utility from seeing the doctor now to your predicted utility from procrastinating. In order to calculate this predicted utility, you must predict when you will eventually decide to have your checkup if you do not do it now. Assume you are a beta-delta discounter with δ = 0.95.
a. In each blank in the first row, indicate whether you would choose that Saturday to go to the doctor if you had not yet gone and were a time-consistent exponential discounter (β =1).
b. In each blank in the second row, indicate whether you would choose that Saturday go to the doctor if you had not yet gone and were a naive time-inconsistent hyperbolic discounter (β = 0.5).
c. In each blank in the third row, indicate whether you would choose that Saturday to go to the doctor if you had not yet gone and were a sophisticated time-inconsistent hyperbolic discounter (β = 0.5).
d. On which day will each type of discounter go to the doctor? Who has a better outcome, the sophisticate or the naif?
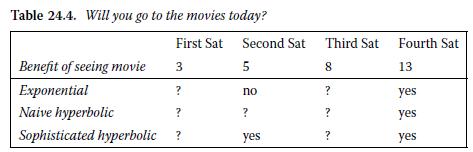
Now assume a different scenario: you need to make three trips to the doctor’s over the next four weeks to get a series of vaccinations. So this month, you can only visit the cinema on one Saturday. Table 24.4 lists the benefits and costs of choosing each particular Saturday to attend the movie, along with several blank rows.
e. In each blank in the first row, indicate whether you would choose that Saturday to watch the movie if you had not seen one yet and were a time-consistent exponential discounter (β =1).
f. In each blank in the second row, indicate whether you would choose that Saturday to watch the movie if you had not seen one yet and were a naive time-inconsistent hyperbolic discounter (β = 0.5).
g. In each blank in the third row, indicate whether you would choose that Saturday to watch the movie if you had not seen one yet and were a sophisticated time inconsistent hyperbolic discounter (β = 0.5).
h. On which day will each type of discounter see the movie? Who has a better outcome, the sophisticate or the naif?
i. Explain why the sophisticated discounter has a better outcome when fighting the urge to procrastinate than when trying to delay gratification. Interpret this outcome in terms of the present self “distrusting” the future self in the case of sophisticated hyperbolic discounting.
Step by Step Answer:






