The following transactions for Kramer Corporation occurred during December of the current year. Follow the step-by-step instructions
Question:
Step 1: Start Integrated Accounting 8e.
Step 2: Open file IA8 Problem 08-B.
Step 3: Enter your name in the Your Name text box.
Step 4: Use Save As to save your file with a file name of 08-BBC Your Name (where 08-B identifies the problem, and BC represents Before Closing).
Step 5: Enter the following journal transactions directly into the General Journal tab.
Dec. 02
Declared and paid an annual dividend of $3.25 per share on the 55,000 shares of common stock outstanding to stockholders of record; Check No. 4253.
04
Received cash on account, covering Sales Invoice No. 3101 for $50,411.00.
05
Declared a 5-percent common stock dividend on common stock outstanding (55,000 × 5% = 2,750 shares). The market value of the common stock is $31.50; Reference, Div.
Before this transaction, 55,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $25.20 were outstanding.
06
Sold merchandise on account, $289,990.00; Sales Invoice No. 3135. The cost of the merchandise sold was $92,796.00.
Problems in previous chapters included businesses that had perputual inventory systems. In those problems, the computer automatically calculated the cost of merchandise from their inventory data, and then automatically integrated the data to the business€™s inventory and accounting systems. Because Kramer Corporation does not use an inventory system, the cost of merchandise sold has been provided in the sales transaction. Therefore, the following journal entry is provided as an example of how to enter this sales transaction in the general journal.
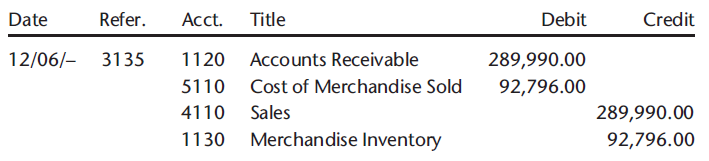
08
Issued the stock certificates for the $69,300,00 common stock dividend declared on December 5th; Reference, Cert.
08
Paid cash on account, $140,665.00; Check No. 4254.
09
Paid for advertising, $7,475.00; Check No. 4255.
09
Received cash on account, covering Sales Invoice No. 3105 for $289,990.00.
11
Purchased merchandise on account, $134,798.00; Invoice No. 5511. (Debit Merchandise Inventory.)
15
Paid additional federal income tax, $35,750.00; Check No. 4256.
15
Paid salaries, $65,565.70; Check No. 4257.
18
Paid utilities, $2,956.00; Check No. 4258.
19
Sold merchandise on account, $175,135.00; Sales Invoice No. 3136. The cost of the merchandise sold was $56,043.20.
21
Paid cash on account, $134,798.00; Check No. 4259.
24
Purchased 2,500 shares of own common stock (treasury stock) at $30.25, recording the stock at cost; Check No. 4260.
27
Purchased merchandise on account, $173,050.00; Invoice No. 5512.
27
Paid monthly rent, $13,000.00; Check No. 4261.
29
Paid miscellaneous expense, $455.00; Check No. 4262.
31
The board of directors authorized an appropriation for treasury stock, $30,000.00; Reference, Treas.
31
The board of directors authorized an appropriation for plant expansion, $300,000.00; Reference, Plant.
Step 6: Display the journal entries and make corrections, if necessary.
Step 7: Display the trial balance.
End-of-Month Activities
Use the following adjustment data for the month of December for Kramer Corporation and the trial balance report as the basis for preparing the adjusting entries.
Inventory of supplies on December 31.............................$7,640.00
Depreciation on equipment for December ........................$810.20
Step 1: Enter the adjusting entries in the general journal. Enter a reference of Adj.Ent. in the Reference text box.
Step 2: Display the adjusting entries.
Step 3: Display the income statement.
Step 4: Display the retained earnings statement.
Step 5: Display the balance sheet.
Step 6: Generate an expense distribution graph.
Step 7: Save your data to disk with a file name of 08-BBC Your Name.
Step 8: Optional spreadsheet integration activity.
Corporations may sell bonds to the investing public to finance operations and expansion. Bonds must be repaid at a certain time and require periodic payments of interest. (In this problem interest will be paid annually.) Use a spreadsheet template to calculate the interest and amortization of a bond issue (sold at a discount) using the effective interest method.
a. Start your spreadsheet software.
b. Open and load the spreadsheet template file: IA8 Spreadsheet 08-B.
c. Enter your name in cell A1.
d. Enter the data about the following bond issue sold at a discount in appropriate cells C5-C9:
Bond Issue: $205,000.00
Carrying Value: $197,179.00
Length (Years): 5
Face Interest Rate: 8.75%
Effective Interest Rate: 9.75%
e. Highlight and copy cells A14-F14 to the clipboard.
f. Highlight and paste the number of the following rows corresponding to the number of years (minus one) of amortization. For example, in this problem highlight and paste the following four rows: A15-F18.
g. Print the completed spreadsheet.
h. Save the spreadsheet to your disk and folder with a file name of 08-
B Your Name. Experiment using different bond issue data.
Step 9: Optional word processing integration activity.
Use the company€™s word processing memorandum template to prepare a memorandum to the accounting department containing the interest and amortization of the bond discount calculated in the spreadsheet.
a. Copy the interest and amortization headings and data for each of the 5 years from the spreadsheet to the clipboard.
b. Start your word processing application software and load template file IA8 Word processing 08-B (load as a document file).
c. Enter your name in the FROM field and complete the remainder of the top portion of the memorandum.
d. Position the insertion point at the location indicated and paste the report. Format the document as necessary.
e. Print the completed document.
f. Save the document to your disk and folder with a file name of 08-B Your Name.
Step 10: Generate and post the closing journal entries.
Step 11: Display the computer-generated closing entries.
Step 12: Display the post-closing trial balance.
Step 13: Save your data with a file name of 08-BAC Your Name (where 08-B identifies the problem, and AC represents After Closing).
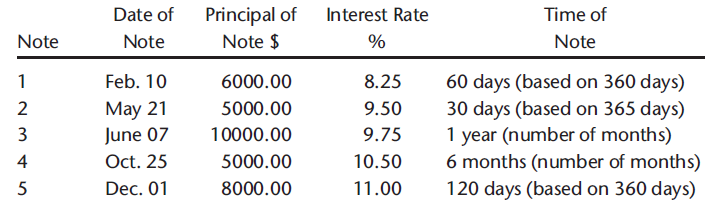
Step 14: Calculate maturity dates, interest, and value on notes.
Use the Notes & Interest Planner to calculate the maturity date, interest, and maturity value for each of the following notes. Use the current year for the date of each note.
Step 15: End the Integrated Accounting 8e session.
Common StockCommon stock is an equity component that represents the worth of stock owned by the shareholders of the company. The common stock represents the par value of the shares outstanding at a balance sheet date. Public companies can trade their stocks on... Corporation
A Corporation is a legal form of business that is separate from its owner. In other words, a corporation is a business or organization formed by a group of people, and its right and liabilities separate from those of the individuals involved. It may... Distribution
The word "distribution" has several meanings in the financial world, most of them pertaining to the payment of assets from a fund, account, or individual security to an investor or beneficiary. Retirement account distributions are among the most... Dividend
A dividend is a distribution of a portion of company’s earnings, decided and managed by the company’s board of directors, and paid to the shareholders. Dividends are given on the shares. It is a token reward paid to the shareholders for their... Maturity
Maturity is the date on which the life of a transaction or financial instrument ends, after which it must either be renewed, or it will cease to exist. The term is commonly used for deposits, foreign exchange spot, and forward transactions, interest... Par Value
Par value is the face value of a bond. Par value is important for a bond or fixed-income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments. The market price of a bond may be above or below par,...
Step by Step Answer:

Integrated Accounting
ISBN: 978-1285462721
8th edition
Authors: Dale A. Klooster, Warren Allen, Glenn Owen





