Question: Redo Listing 7.7, modifying the three array-handling functions to each use two pointer parameters to represent a range. The fill_array() function, instead of returning the
Redo Listing 7.7, modifying the three array-handling functions to each use two pointer parameters to represent a range. The fill_array() function, instead of returning the actual number of items read, should return a pointer to the location after the last location filled; the other functions can use this pointer as the second argument to identify the end of the data.
![Max = 5; // function prototypes int fill_array (double ar [], int](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1662/0/1/4/7656310552dcd0ff1662014765634.jpg)
Here are two sample runs of the program in Listing 7.7:
Enter value #1: 100000
Enter value #2: 80000
Enter value #3: 222000
Enter value #4: 240000
Enter value #5: 118000
Property #1: $100000
Property #2: $80000
Property #3: $222000
Property #4: $240000
Property #5: $118000
Enter revaluation factor: 0.8
Property #1: $80000
Property #2: $64000
Property #3: $177600
Property #4: $192000
Property #5: $94400
Done.
Enter value #1: 200000
Enter value #2: 84000
Enter value #3: 160000
Enter value #4: -2
Property #1: $200000
Property #2: $84000
Property #3: $160000
Enter reevaluation factor: 1.20
Property #1: $240000
Property #2: $100800
Property #3: $192000
Done.
Recall that fill_array() prescribes that input should quit when the user enters five properties or enters a negative number, whichever comes first. The first output example illustrates reaching the five-property limit, and the second output example illustrates that entering a negative value terminates the input phase.
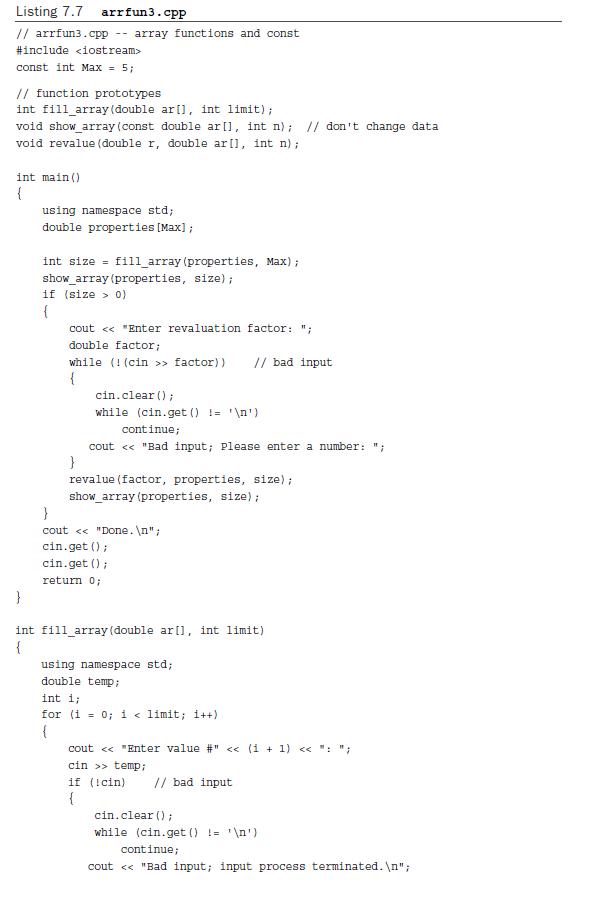
Listing 7.7 arrfun3.cpp // arrfun3.cpp array functions and const #include const int Max = 5; // function prototypes int fill_array (double ar [], int limit); void show_array(const double ar [], int n); // don't change data void revalue (double r, double ar [], int n) ; int main() { using namespace std; double properties [Max]; int size = fill_array (properties, Max); show_array (properties, size); if (size > 0) { cout < < "Enter revaluation factor: "; double factor; while (!(cin >> factor)) // bad input { cin.clear(); while (cin.get () != ' ') continue; cout < < "Bad input; Please enter a number: "; } revalue (factor, properties, size); show_array (properties, size); } cout < < "Done. "; cin.get(); cin.get(); return 0; } int fill_array(double ar [], int limit) { using namespace std; double temp; int i; for (i = 0; i < limit; i++) { cout < < "Enter value #" < < (1 + 1) < < ": "; cin >> temp; if (cin) // bad input { cin.clear(); while (cin.get () != ' ') continue; cout < < "Bad input; input process terminated. ";
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The modified version of Listing 77 uses two pointer parameters to represent a range in the three arrayhandling functions The fillarray function would ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


