Question: We can generalize the 1-dimensional discrete Fourier transform defined by equation (30.8) to d dimensions. The input is a d-dimensional array A = (a j
We can generalize the 1-dimensional discrete Fourier transform defined by equation (30.8) to d dimensions. The input is a d-dimensional array A = (aj1,j2,...,jd)?whose dimensions are?n1, n2, . . . ,nd, where?n1n2 . . .?nd =?n. We define the?d-dimensional discrete Fourier transform by the equation
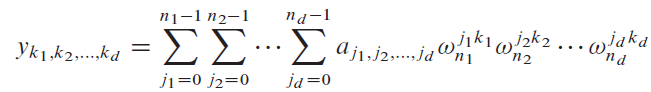
for
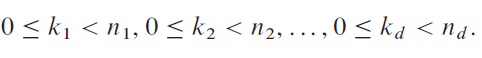
a. Show that we can compute a d-dimensional DFT by computing 1-dimensional DFTs on each dimension in turn. That is, we first compute n/n1 separate?1-dimensional DFTs along dimension?1. Then, using the result of the DFTs along dimension?1?as the input, we compute?n/n2 separate?1-dimensional DFTs along dimension?2. Using this result as the input, we compute?n/n3 separate?1-dimensional DFTs along dimension?3, and so on, through dimension?d.
b.?Show that the ordering of dimensions does not matter, so that we can compute a?d-dimensional DFT by computing the?1-dimensional DFTs in any order of the?d?dimensions.
c. Show that if we compute each 1-dimensional DFT by computing the fast Fourier transform, the total time to compute a d-dimensional DFT is O(n lg n), independent of d.
0 < k1 < n1, 0 < k2 < n2, .., 0 < ka < na.
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a To compute a ddimensional DFT we can use the following algorithm 1 Compute nn1 separate 1dimension... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


