Question: In this problem, we would like to find the PDFs of order statistics. Let X 1 ,,X n be a random sample from a continuous
In this problem, we would like to find the PDFs of order statistics. Let X1,…,Xn be a random sample from a continuous distribution with CDF FX(x) and PDF fX(x). Define X(1),…,X(n) as the order statistics. Our goal here is to show that![fx(i)(x) = = n! fx(x) [Fx(x)] [1 - Fx(z)]". (i-1)! (ni)! *](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1698/3/0/7/434653a1d6a789341698307432727.jpg)
One way to do this is to differentiate the CDF (found in Problem 9). However, here, we would like to derive the PDF directly. Let fX(i) (x) be the PDF of X(i). By definition of the PDF, for small δ, we can write 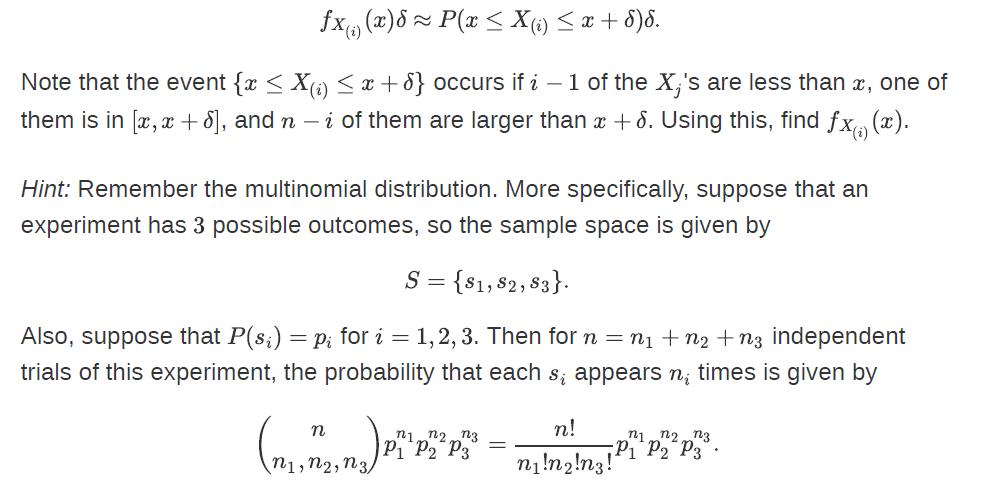
Problem 9
In this prob lem, we would like to find the CDFs of the order statistics. Let X1,…,Xn be a random sample from a continuous distribution with CDF FX(x) and PDF fX(x).
Define X(1),…,X(n) as the order statistics and show that![n Fxs) (x) = (7) [Fx(2)] * [1 Fx(x)]*-*. (i) k k=i](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1698/3/0/7/302653a1ce620bfc1698307300474.jpg)
Fix x ∈ R. Let Y be a random variable that counts the number of Xj's ≤ x. Define {Xj ≤ x} as a "success" and {Xj > x} as a "failure," and show that Y ∼ Binomial(n, p = FX(x)).
fx(i)(x) = = n! fx(x) [Fx(x)] [1 - Fx(z)]". (i-1)! (ni)! *
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


