Question: A count random variable, say Y, takes on nonnegative integer values, {0, 1, 2, . . .}. The most common distribution for a count variable
A count random variable, say Y, takes on nonnegative integer values, {0, 1, 2, . . .}. The most common distribution for a count variable is the Poisson(θ) distribution, where the parameter u is the expected value: θ = E(Y). The probability density function is
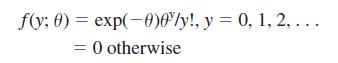
It can be shown that Var(Y) = θ, so that the mean and variance are the same.
(i) For a random draw Yi from the population, find the log-likelihood function ℓ(θ; Yi) = log[f(Yi; θ)].
What is the log likelihood for a random sample of size n, say Ln(θ)?
(ii) Using the notational convention in Section C.7, find the first order condition for the MLE, u^
θ̂, and show that θ̂ = Y̅, the sample average.
(iii) Why is θ̂ unbiased?
(iv) Find Var(Y) as a function of u and n.
(v) Why is Y consistent?
(vi) Do the unbiasedness and consistency of the MLE in this case depend on whether the Poisson distribution is correct? Explain.
(vii) What is the distribution of
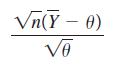
as n → ∞? Explain.
(viii) If E(Y) = θ but Var(Y) = v(θ) . 0—so that the Poisson distribution may fail—modify the random variable in (vii) so that it has a limiting distribution that does not depend on u.
f(y; 0) = exp(-0)0'ly!, y = 0, 1, 2, ... = 0 otherwise
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
i The loglikelihood function for a single random draw Yi from the Poisson distribution is Yi logfYi ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


