In the STAR experiment, Example 7.8, children were randomly assigned within schools into three types of classes:
Question:
In the STAR experiment, Example 7.8, children were randomly assigned within schools into three types of classes: small classes with 13-17 students, regular-sized classes with 22-25 students, and regular-sized classes with a full-time teacher aide to assist the teacher. Student scores on achievement tests were recorded as well as some information about the students, teachers, and schools. Data for the kindergarten classes is contained in the data file star5_small2.
a. Regress MATHSCORE on SMALL, AIDE, TCHEXPER, SCHRURAL, FREELUNCH, and BOY. Test for heteroskedasticity related to \(S M A L L\) and \(A I D E\) using the \(N R^{2}\) test. What do you conclude at the \(5 \%\) level?
b. Estimate the regression model in (a) by OLS including interactions between FREELUNCH and the other variables. Test for heteroskedasticity related to \(S M A L L\) and \(A I D E\) using the \(N R^{2}\) test. What do you conclude at the \(5 \%\) level?
c. Using the model in (b), and both conventional and robust standard errors, test the joint significance of the interactions between FREELUNCH and SMALL, AIDE, and TCHEXPER at the \(10 \%\) level in each regression. What do you conclude?
d. Estimate the model in (b) and include indicator variables for each school (SCHOOLID). Test for heteroskedasticity related to SMALL and AIDE using the \(N R^{2}\) test. What do you conclude at the \(5 \%\) level?
e. Using the model in (d), and both conventional and robust standard errors, test the joint significance of the interactions between FREELUNCH and SMALL, AIDE, and TCHEXPER at the \(10 \%\) level in each regression. What do you conclude?
Data From Example 7.8:-
Medical researchers use white mice to test new drugs because these mice, surprisingly, are genetically similar to humans. Mice that are bred to be identical are randomly assigned to treatment and control groups, making estimation of the treatment effect of a new drug on the mice a relatively straightforward and reproducible process. Medical research on humans is strictly regulated, and volunteers are given incentives to participate, then randomly assigned to treatment and control groups. Randomized controlled experiments in the social sciences are equally attractive from a statistician's point of view but are rare because of the difficulties in organizing and funding them. A notable example of a randomized experiment is Tennessee's Project STAR. \({ }^{15}\)
A longitudinal experiment was conducted in Tennessee beginning in 1985 and ending in 1989. A single cohort of students was followed from kindergarten through third grade. In the experiment, children were randomly assigned within schools into three types of classes: small classes with 13-17 students, regular-sized classes with 22-25 students, and regular-sized classes with a full-time teacher aide to assist the teacher. Student scores on achievement tests were recorded, as was some information about the students, teachers, and schools. Data for the kindergarten classes is contained in the data file star.
Let us first compare the performance of students in small classes versus regular classes. \({ }^{16}\)
The variable TOTALSCORE is the combined reading and math achievement scores and \(S M A L L=1\) if the student was assigned to a small class, and zero if the student is in a regular class. In Table 7.6a and b are summary statistics for the two types of classes. First, note that on all measures except TOTALSCORE the variable means reported are very
similar. This is because students and teachers were randomly assigned to the classes, so that there should be no patterns evident. The average value of TOTALSCORE in the regular classes is 918.0429 and in small classes it is 931.9419, a difference of 13.899 points. The test scores are higher in the smaller classes. The difference estimator obtain using regression will yield the same estimate, along with significance levels.
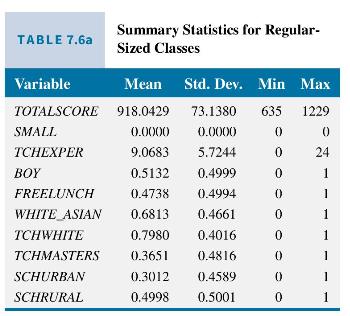
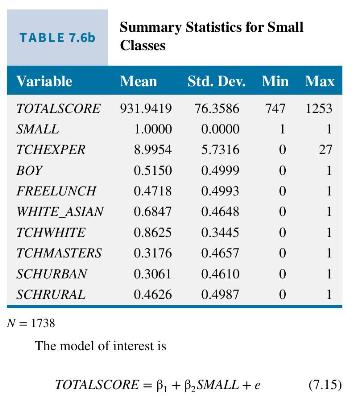
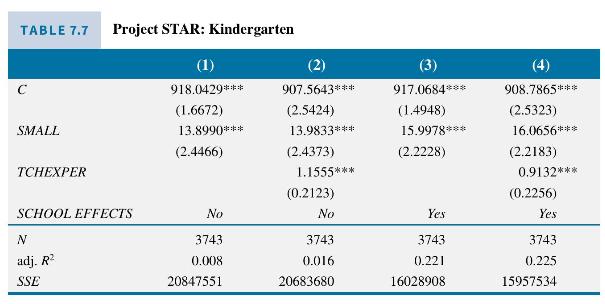
The regression results are in column (1) of Table 7.7. The estimated "treatment effect" of putting kindergarten children into small classes is 13.899 points, the same as the difference in sample means computed above, on their achievement score total; the difference is statistically significant at the 0.01 level.
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Econometrics
ISBN: 9781118452271
5th Edition
Authors: R Carter Hill, William E Griffiths, Guay C Lim





