Using the NLS panel data on (N=716) young women for years 1982, 1983, 1985, 1987, and 1988,
Question:
Using the NLS panel data on \(N=716\) young women for years 1982, 1983, 1985, 1987, and 1988, we are interested in the relationship between \(\ln (W A G E)\) and education, experience, its square, usual hours worked per week, and an indicator variable for black women. The equation is
\[\ln \left(W A G E_{i t}\right)=\beta_{1}+\beta_{2} E D U C_{i}+\beta_{3} E X P E R_{i t}+\beta_{4} E X P E R_{i t}^{2}+\beta_{5} H O U R S_{i t}+\beta_{6} \text { BLACK }_{i}+u_{i}+e_{i t}\]
Table 15.13 contains OLS, random effects, and Hausman-Taylor model estimates for this model and includes conventional and cluster-robust standard errors for each. The Hausman-Taylor estimator treats EDUC and HOURS as endogenous and correlated with the unobserved heterogeneity.
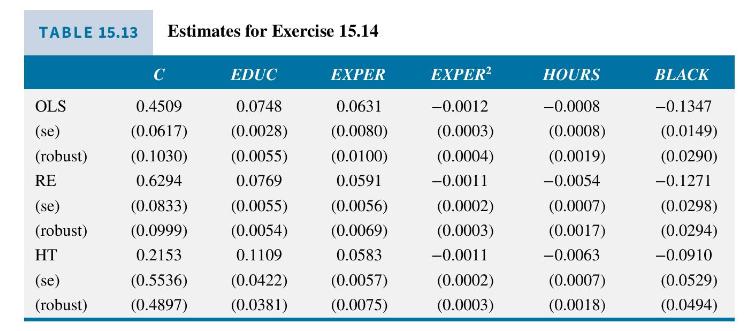
a. What is the interpretation of \(\beta_{2}\) ? How much difference is there among the OLS, random effects, and Hausman-Taylor estimates of \(\beta_{2}\) ? Construct a 95\% interval estimate for \(\beta_{2}\) using each estimator and cluster-robust standard errors. What differences do you observe?
b. For the Hausman-Taylor estimator, how many instrumental variables are required? How many instruments do we have? What are they?
c. For this model, why might we prefer the Hausman-Taylor estimator to the fixed effects estimator?
d. The fixed effects estimates of the coefficients of EXPER, EXPER \({ }^{2}\), and HOURS and their conventional standard errors are \(0.0584(0.00574),-0.0011(0.00023)\), and \(-0.0063(0.00074)\), respectively. Comparing these estimates to the random effects estimates, with conventional standard errors, are we justified in worrying about endogeneity in this model?
e. By using cluster-robust standard errors for the random effects estimator, which of the assumptions RE1-RE5 are we relaxing?
f. Using the Hausman-Taylor model, \(\hat{\sigma}_{u}=0.35747\) and \(\hat{\sigma}_{e}=0.19384\). Given these estimates, which source of error variation is more important in this model? The variation in unobserved heterogeneity or the variation in the idiosyncratic error? What is the proportion of the combined variation that is accounted for by the unobserved heterogeneity?
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Econometrics
ISBN: 9781118452271
5th Edition
Authors: R Carter Hill, William E Griffiths, Guay C Lim





