Question: Example 2 in Section 4.8 displayed a low-pass linear filter that changed a signal {y k } into {y k+1 } and changed a higher-frequency
Example 2 in Section 4.8 displayed a low-pass linear filter that changed a signal {yk} into {yk+1} and changed a higher-frequency signal {ωk} into the zero signal, where yk = cos(πk/4) and (ωk) = cos(3πk/4). The following calculations will design a filter with approximately those properties. The filter equation is
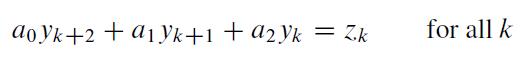
Write an equation Ax = b, where A is a 16 x 3 matrix formed from the two coefficient matrices above and where b in R16 is formed from the two right sides of the equations. Find a0, a1, and a2 given by the least-squares solution of Ax = b. (The .7 in the data above was used as an approximation for √2/2, to illustrate how a typical computation in an applied problem might proceed. If .707 were used instead, the resulting filter coefficients would agree to at least seven decimal places with √2/4; 1/2, and √2/4, the values produced by exact arithmetic calculations.)
Data From Example 2 in Section 4.8
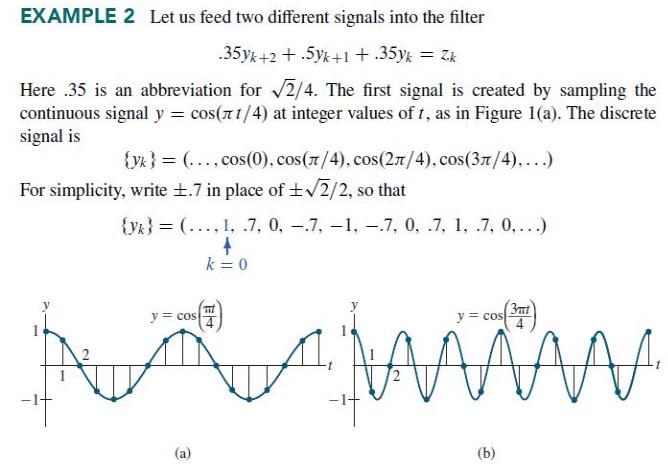
aoyk+2a1Yk+1 + ayk = Zk for all k
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To find the leastsquares solution for the filter coefficients a0 a1 and a2 we need to construct the matrix equation Ax b where A is a 16 x 3 matrix fo... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


