The wings of a glider are each 4 m long. The loadbearing member is the wing spar,
Question:
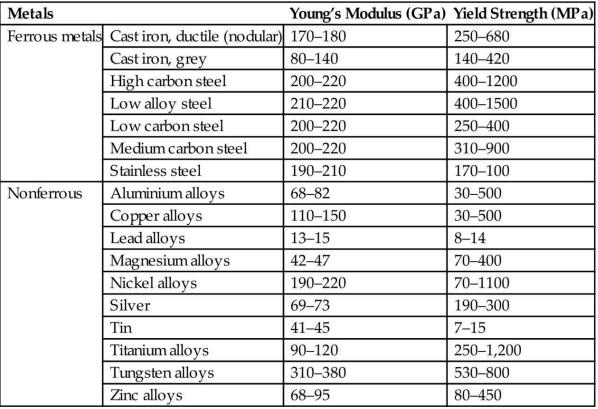
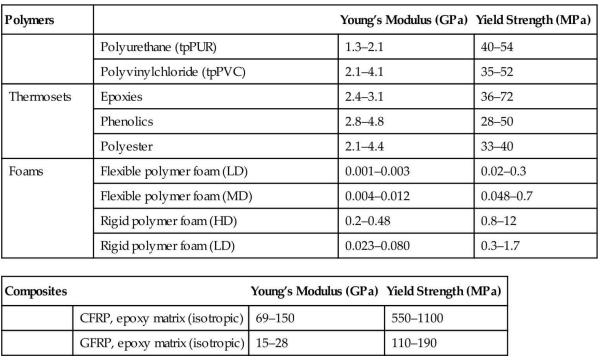
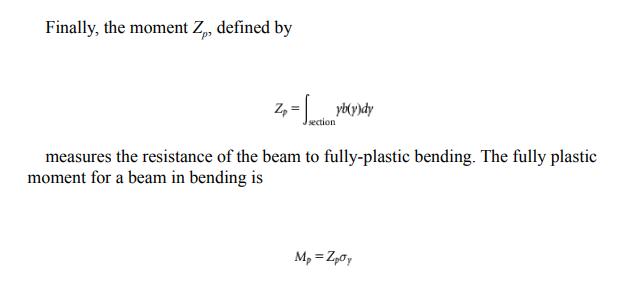
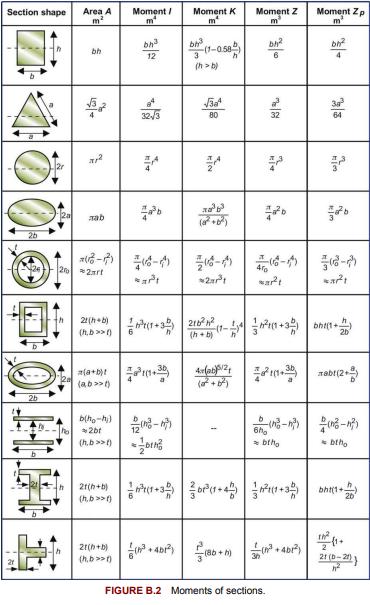
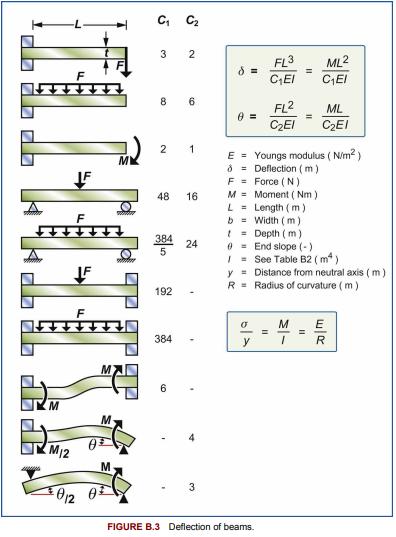
The wings of a glider are each 4 m long. The loadbearing member is the wing spar, a tubular beam running the length of the wing. The wing spar in this glider has a diameter of 140 mm and a wall thickness of 6 mm. It is made of an aluminum alloy. In flight the wing spar is loaded in bending with (we will assume) a uniformly distributed force per unit length. By how much will the wing tip deflect in calm flight if the loaded glider weighs 1000 kg? Use data from Appendix A3 for the (mean) value of Young’s modulus of aluminum alloys, the equation for the elastic deflection of a cantilever from Appendix B3 and for the second moment of a beam from Appendix B2 to find out.
Data From Appendix A3

Data From Appendix B2


Data From Appendix B3
When a beam is loaded by a force F or moments M, the initially straight axis is deformed into a curve. If the beam is uniform in section and properties, long in relation to its depth and nowhere stressed beyond the elastic limit, the deflection , and the angle of rotation, can be calculated using elastic beam theory. The basic differential equation describing the curvature of the beam at a point x along its length is
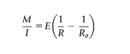
where y is the lateral deflection, and M is the bending moment at the point x on the beam. E is Young’s modulus and I is the second moment of area. When M is constant this becomes


Step by Step Answer:






