Selected transactions completed by Gampfer Company during its first fiscal year ending December 31 were as follows:
Question:
December 31 were as follows:
Jan. 2. Issued a check to establish a petty cash fund of $3,200.
Mar. 14. Replenished the petty cash fund, based on the following summary of petty
cash receipts: office supplies, $1,200; miscellaneous selling expense, $410;
miscellaneous administrative expense, $620.
Apr. 21. Purchased $22,400 of merchandise on account, terms 1/10, n/30. The perpetual inventory system is used to account for inventory.
May 20. Paid the invoice of April 21 after the discount period had passed.
23. Received cash from daily cash sales for $15,120. The amount indicated by the
cash register was $15,152.
June 15. Received a 60-day, 10% note for $127,500 on the Cady account.
Aug. 14. Received amount owed on June 15 note, plus interest at the maturity date.
18. Received $5,440 on the Yoder account and wrote off the remainder owed
on a $6,400 accounts receivable balance. (The allowance method is used in
accounting for uncollectible receivables.)
Sept. 9. Reinstated the Yoder account written off on August 18 and received $960 cash
in full payment.
15. Purchased land by issuing a $480,000, 90-day note to Ace Development Co.,
which discounted it at 8%.
Oct. 17. Sold office equipment in exchange for $96,000 cash plus receipt of a $64,000,
90-day, 6% note. The equipment had a cost of $224,000 and accumulated
depreciation of $44,800 as of October 17.
Nov. 30. Journalized the monthly payroll for November, based on the following data:
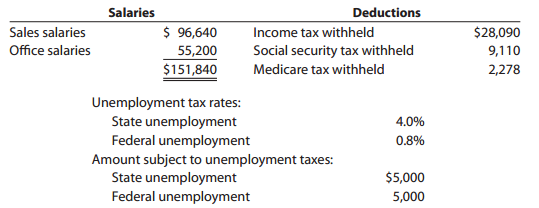
30. Journalized the employer€™s payroll taxes on the payroll.
Dec. 14. Journalized the payment of the September 15 note at maturity.
31. The pension cost for the year was $136,000, of which $99,840 was paid to the
pension plan trustee.
1. Journalize the selected transactions.
2. Based on the following data, prepare a bank reconciliation for December of the
current year:
a. Balance according to the bank statement at December 31, $202,240.
b. Balance according to the ledger at December 31, $175,440.
c. Checks outstanding at December 31, $48,960.
d. Deposit in transit, not recorded by bank, $21,120.
e. Bank debit memo for service charges, $540.
f. A check for $11,520 in payment of an invoice was incorrectly recorded in the accounts
as $11,020.
3. Based on the bank reconciliation prepared in (2), journalize the entry or entries to be
made by Gampfer Company.
4. Based on the following selected data, journalize the adjusting entries as of December
31 of the current year:
a. Estimated uncollectible accounts at December 31, $11,520, based on an aging of
accounts receivable. The balance of Allowance for Doubtful Accounts at December
31 was $1,200 (debit).
b. The physical inventory on December 31 indicated an inventory shrinkage of $2,360.
c. Prepaid insurance expired during the year, $16,300.
d. Office supplies used during the year, $2,800.
e. Depreciation is computed as follows:
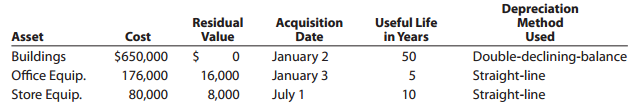
f. A patent costing $36,000 when acquired on January 2 has a remaining legal life of
eight years and is expected to have value for six years.
g. The cost of mineral rights was $390,000. Of the estimated deposit of 650,000 tons
of ore, 38,400 tons were mined and sold during the year.
h. Vacation pay expense for December, $7,500.
i. A product warranty was granted beginning December 1 and covering a one-year
period. The estimated cost is 3% of sales, which totaled $1,350,000 in December.
j. Interest was accrued on the note receivable received on October 17.
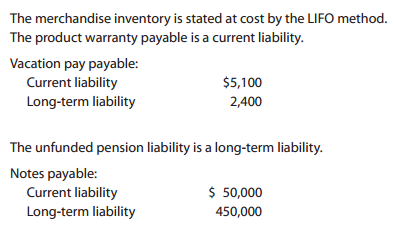
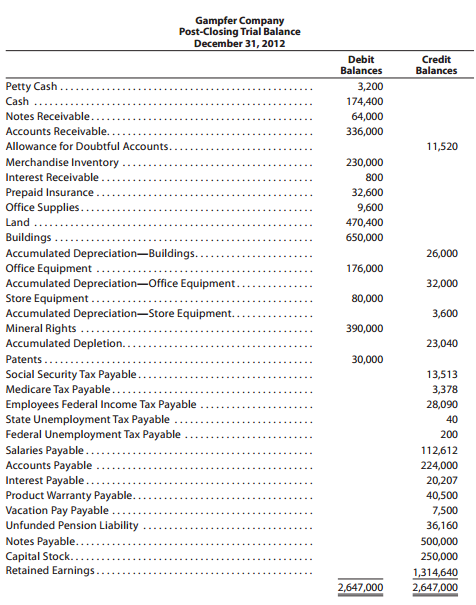
5. Based on the following information and the post-closing trial balance shown on the following page, prepare a balance sheet in report form at December 31 of the current year.
Accounts receivables are debts owed to your company, usually from sales on credit. Accounts receivable is business asset, the sum of the money owed to you by customers who haven’t paid.The standard procedure in business-to-business sales is that... Balance Sheet
Balance sheet is a statement of the financial position of a business that list all the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity and shareholder’s equity at a particular point of time. A balance sheet is also called as a “statement of financial... Maturity
Maturity is the date on which the life of a transaction or financial instrument ends, after which it must either be renewed, or it will cease to exist. The term is commonly used for deposits, foreign exchange spot, and forward transactions, interest...
Step by Step Answer:

Financial and Managerial Accounting Using Excel for Success
ISBN: 978-1111993979
1st edition
Authors: James Reeve, Carl S. Warren, Jonathan Duchac





