Question: Consider the potentially stiff system For large values, the system becomes stiff as it contains components that vary with different speeds, i.e. y 2
Consider the potentially stiff system![dyi dt dy2 = -yi(t), = -y(t), dt y (0) = 1, 1/2 (0) = 1, t = [0, 1]. The analytical solution to this problem](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/0/0/3576556ffa5984411700200357110.jpg)
For large α values, the system becomes stiff as it contains components that vary with different speeds, i.e. y2(t) approaches zero much faster than y1(t) does. The solutions to this problem for α = 2 and α = 200 000 are shown in Figure 6.11. By analyzing the
number of steps required by the different methods, it becomes clear how the stiff solvers outperform the explicit methods. Calculations have been performed for different values of α with different error tolerances; the results are summarized in Table 6.4.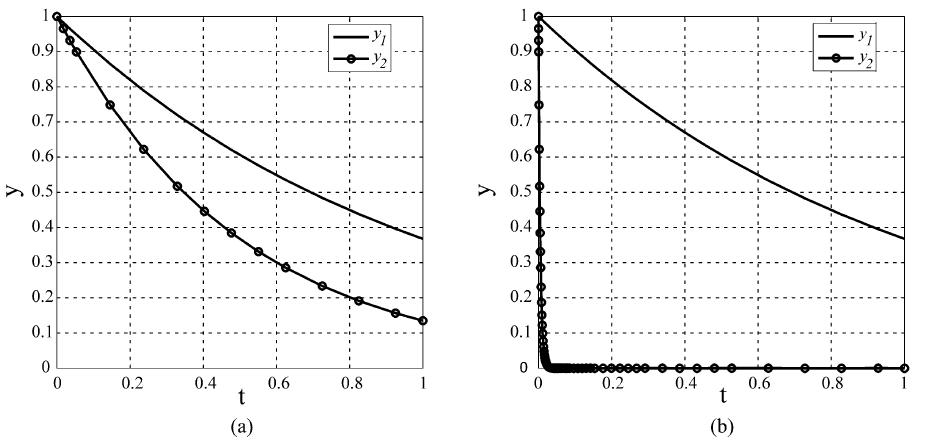
Table 6.4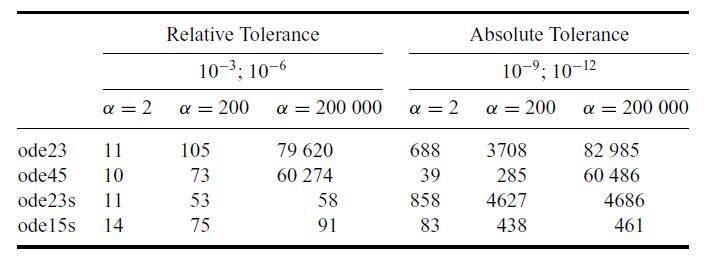
dyi dt dy2 = - y(t), = -y(t), dt y (0) = 1, 1/2 (0) = 1, t = [0, 1]. The analytical solution to this problem is given by Syr(t) =et, (1(t) = e-at
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


