Question: Show that the examples given in Example 26.5 are indeed inner product spaces. Data from example 26.5 Example 26.5 (1) The typical finite-dimensional R (R-vector
Show that the examples given in Example 26.5 are indeed inner product spaces.
Data from example 26.5
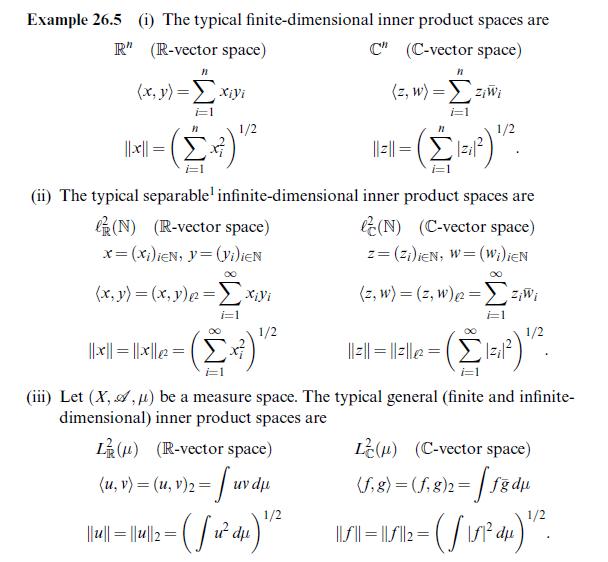

Example 26.5 (1) The typical finite-dimensional R" (R-vector space) n (x, y) = xiyi i=1 1/2 Ball= (x) / ||x|| i=1 (ii) The typical separable infinite-dimensional (N) (R-vector space) x=(Xi)ieN, }=(Vi)ieN (x, y) = (x, y) = xyi ||u| i=1 = (x 1/2 L() (R-vector space) (u, v) = (u, v)2 = uv du = fuvd [ inner product spaces are C" (C-vector space) (z, w) = z;Wi i=1 11 ||2||=> ||x||=||x||= (iii) Let (X, A, ) be a measure space. The typical general (finite and infinite- dimensional) inner product spaces are 1/2 i=1 inner product spaces are (N) (C-vector space) z = (Zi) iEN, W=(Wi)EN (z, w) = (z, w) = z;W E1 1/2 - (1=) . |||||=||||e= 1/2 |-|(4)-11/12 (15741) " du d L() (C-vector space) (f.g) = (f.g)2= |fgdu 58)2 = [8 d
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Data from remark 135 Equation 133 If we set d X 1 2n A P... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


