Emily purchases food (measured by x) and clothing (measured by y). Her preferences are described by the
Question:
Emily purchases food (measured by x) and clothing (measured by y). Her preferences are described by the quasilinear utility function U(x, y) 32 √x 2y, with
MUx = 16 / √x and MUy = 2. Throughout this problem, the prices of the two goods are Px = 2, Py = 1. Emily has a monthly income of I.
a) Show that Emily has a diminishing marginal rate of substitution of food for clothing.
b) Show that, as long as I ≥ 32, Emily always purchases the same amount of food each month. When I ≥ 32, how many units does she buy?
c) Fill in the following table with the amounts of food and clothing and the level of utility she realizes at the three levels of income shown.
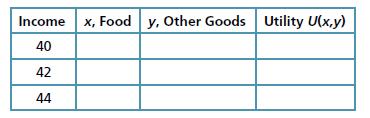
d) What do the numbers in the table tell you about the marginal utility of income (ΔU/ΔI) as income rises from 40 to 2? What is the marginal utility of income when income increases from 42 to 44?
e) In Chapter 4, we showed how to use the method of Lagrange to solve the consumer choice problem:
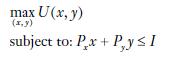
We also demonstrated that the value of the Lagrange multiplier, λ, measures the consumer’s marginal utility of income. Assuming Px = 2, Py = 1, and I ≥ 32, find the value of the Lagrange multiplier. Show that it does not vary with income, and verify that the value of the Lagrange multiplier is the same as the values of the marginal utility of income you calculated in part (d).
Step by Step Answer:






