Question: Consider a point P in the curved interface between two fluids. Introduce Cartesian coordinates at P with x and y parallel to the interface and
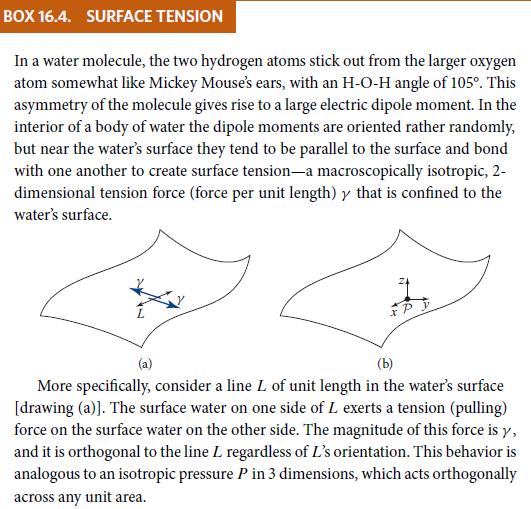
Consider a point P in the curved interface between two fluids. Introduce Cartesian coordinates at P with x and y parallel to the interface and z orthogonal [as in diagram (b) in Box 16.4], and orient the x- and y-axes along the directions of the interface’s principal curvatures, so the local equation for the interface is

Here R1 and R2 are the surface’s principal radii of curvature at P; note that each of them can be positive or negative, depending on whether the surface bends up or down along their directions. Show that, in equilibrium, stress balance, ∇ · T = 0, for the surface implies that the pressure difference across the surface is
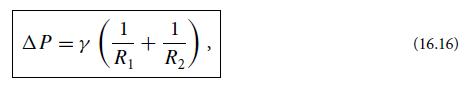
where γ is the surface tension.

Z= x y + 2R 2R (16.15)
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To derive the pressure difference across a curved interface between two fluids we use the concept of ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


