Question: Consider a simple refracting telescope (Fig. 7.7) that comprises two converging lenses, the objective and the eyepiece. This telescope takes parallel rays of light from
Consider a simple refracting telescope (Fig. 7.7) that comprises two converging lenses, the objective and the eyepiece. This telescope takes parallel rays of light from distant stars, which make an angle θ ≪ 1with the optic axis, and converts them into parallel rays making a much larger angle Mθ. Here M is the magnification with М negative, |M| >> 1, and |Mθ|≪ 1. (The parallel output rays are then focused by the lens of a human’s eye, to a point on the eye’s retina.)
(a) Use matrix methods to investigate how the output rays depend on the separation of the two lenses, and hence find the condition that the output rays are parallel when the input rays are parallel.
(b) How does the magnification M depend on the ratio of the focal lengths of the two lenses?
(c) If, instead of looking through the telescope with one’s eye, one wants to record the stars’ image on a photographic plate or CCD, how should the optics be changed?
Fig. 7.7
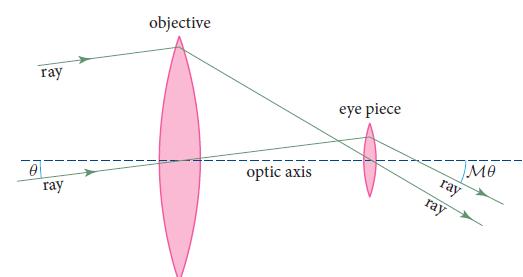
0 ray ray objective optic axis eye piece ray ray Me
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
ANSWER a To investigate how the output rays depend on the separation of the two lenses we can use matrix methods Lets denote the focal length of the o... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


