Question: Show that the Euler-Lagrange equation for the action principle (27.8) is equivalent to the geodesic equation for a photon in the static spacetime metric g
Show that the Euler-Lagrange equation for the action principle (27.8) is equivalent to the geodesic equation for a photon in the static spacetime metric g00(xk), gij(xk). Specifically, do the following.
(a) The action (27.8) is the same as that for a geodesic in a 3-dimensional space with metric γjk and with t playing the role of proper distance traveled [Eq. (25.19) converted to a positive-definite, 3-dimensional metric]. Therefore, the Euler- Lagrange equation for Eq. (27.8) is the geodesic equation in that (fictitious) space [Eq. (25.14) with t the affine parameter]. Using Eq. (24.38c) for the connection coefficients, show that the geodesic equation can be written in the form
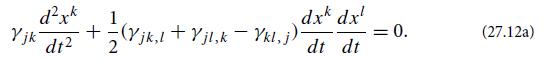
(b) Take the geodesic equation (25.14) for the light ray in the real spacetime, with spacetime affine parameter ζ, and change parameters to coordinate time t. Thereby obtain
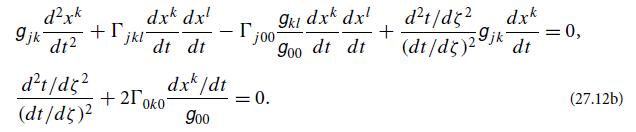
(c) Insert the second of these equations into the first, and write the connection coefficients in terms of derivatives of the spacetime metric. With a little algebra, bring your result into the form Eq. (27.12a) of the Fermat-principle Euler-Lagrange equation.
Equations.

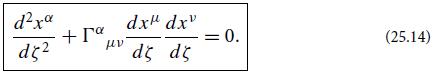
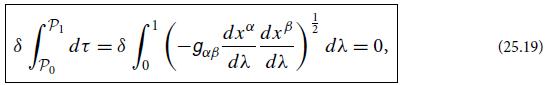
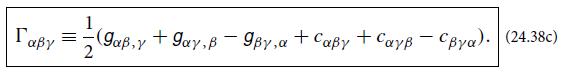
dxk Yjk dt 1 - -/- (Yjk,l + Y jl,k - Ykl, j) = 0. dxk dx dt 2 dt (27.12a)
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To show the equivalence between the EulerLagrange equation for the action principle and the geodesic equation for a photon in a static spacetime metri... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


