Question: Repeat Example 6.4 but let the collision be totally inelastic. Data from Example 6.4 Consider a collision between the two carts of Table 6.1, starting
Repeat Example 6.4 but let the collision be totally inelastic.
Data from Example 6.4
Consider a collision between the two carts of Table 6.1, starting from the same initial velocities, but with \(v_{\mathrm{E} 1 x, \mathrm{f}}=+0.30 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\). Make a table like Table 6.1 for this situation, and compare the amount of kinetic energy converted to internal energy in the Earth reference frame and in a reference frame \(\mathrm{M}\) moving at \(-0.20 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) relative to the track.
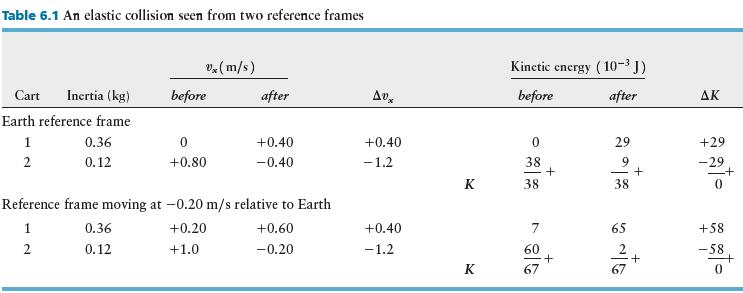
Table 6.1 An elastic collision seen from two reference frames vx (m/s) Kinetic energy (10- J) Cart Inertia (kg) before after Avx before after AK Earth reference frame 1 0.36 0 +0.40 +0.40 0 29 +29 2 0.12 +0.80 -0.40 -1.2 38 9 -29 + + K 38 38 0 Reference frame moving at -0.20 m/s relative to Earth 1 0.36 +0.20 +0.60 2 0.12 +1.0 -0.20 +0.40 65 +58 -1.2 60 -58 + + K 67 67 0
Step by Step Solution
3.53 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


