Question: The expression I derived in Example 29.6 indicates that the emf becomes negative after the solenoid has rotated (180^{circ}) and remains negative through the next
The expression I derived in Example 29.6 indicates that the emf becomes negative after the solenoid has rotated \(180^{\circ}\) and remains negative through the next \(180^{\circ}\) of rotation. However, the solenoid orientation looks the same when the solenoid has rotated \(180^{\circ}\) as when it started. Why does the emf have a different sign for half of the rotation?
Data from Example 29.6
In an electric generator a solenoid that contains \(N\) windings each of area \(A\) is rotated at constant rotational speed \(\omega\) in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude \(B\) (Figure 29.29). What is the emf induced in the solenoid?
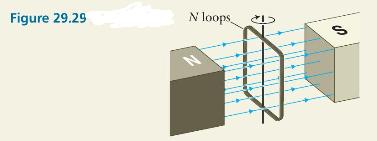
Figure 29.29 N loops,
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Although the solenoid orientation looks the ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


