Question: Multiple-Concept Example 4 deals with the same concepts as this problem. A 41-cm length of wire has a mass of 6.0 g. It is stretched
Multiple-Concept Example 4 deals with the same concepts as this problem. A 41-cm length of wire has a mass of 6.0 g. It is stretched between two fixed supports and is under a tension of 160 N. What is the fundamental frequency of this wire?
Concept Example 4
The heaviest string on an electric guitar has a linear density of 5.28 × 10–3 kg/m and is stretched with a tension of 226 N. This string produces the musical note E when vibrating along its entire length in a standing wave at the fundamental frequency of 164.8 Hz.
(a) Find the length L of the string between its two fixed ends (see Figure 17.17a).
(b) A guitar player wants the string to vibrate at a fundamental frequency of 2 × 164.8 Hz = 329.6 Hz, as it must if the musical note E is to be sounded one octave higher in pitch. To accomplish this, he presses the string against the proper fret before plucking the string. Find the distance L between the fret and the bridge of the guitar (see Figure 17.17b).
Reasoning
The series of natural frequencies (including the fundamental) for a string fixed at both ends is given by fn = nυ/(2L) (Equation 17.3), where n = 1, 2, 3, etc. This equation can be solved for the length L. The speed υ at which waves travel can be obtained from the tension and the linear density of the string. The fundamental frequencies that are given correspond to n = 1.
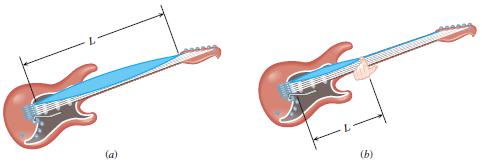
(a) (b)
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
REASONING Equation 173 with n 1 gives the fundamental frequency as f 1 v2... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


