Question: Explain how the Mean Value Theorem (Section 4.2, Theorem 4) is a special case of Taylors Theorem. THEOREM 4-The Mean Value Theorem Suppose y =
Explain how the Mean Value Theorem (Section 4.2, Theorem 4) is a special case of Taylor’s Theorem.
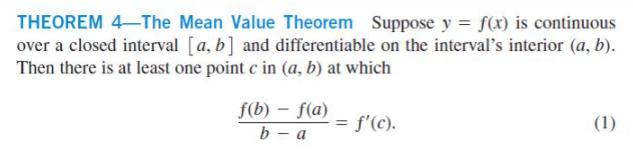
THEOREM 4-The Mean Value Theorem Suppose y = f(x) is continuous over a closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the interval's interior (a, b). Then there is at least one point c in (a, b) at which f(b) f(a) b-a = f'(c). (1)
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The Mean Value Theorem and Taylors Theorem are two important results in calculus that relate the behavior of a function to its derivatives The Mean Va... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


