Question: Galileo developed a formula for a bodys velocity during free fall by rolling balls from rest down increasingly steep inclined planks and looking for a
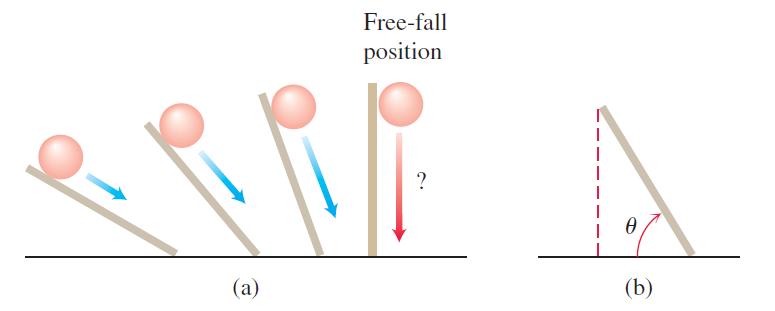
Galileo developed a formula for a body’s velocity during free fall by rolling balls from rest down increasingly steep inclined planks and looking for a limiting formula that would predict a ball’s behavior when the plank was vertical and the ball fell freely; see part (a) of the accompanying figure. He found that, for any given angle of the plank, the ball’s velocity t sec into motion was a constant multiple of t. That is, the velocity was given by a formula of the form y = kt. The value of the constant k depended on the inclination of the plank.
In modern notation—part (b) of the figure—with distance in meters and time in seconds, what Galileo determined by experiment was that, for any given angle u, the ball’s velocity t sec into the roll was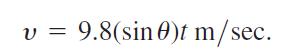
a. What is the equation for the ball’s velocity during free fall?
b. Building on your work in part (a), what constant acceleration does a freely falling body experience near the surface of Earth?
v = 9.8(sin0)t m/sec.
Step by Step Solution
3.21 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The equation for the balls velocity during free fall according ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


