Question: Pearsons theorem for 2 2 contingency tables. Consider the situation of Theorem (11.18) for the case a D b D 2 and show the following.
Pearson’s theorem for 2 2 contingency tables. Consider the situation of Theorem
(11.18) for the case a D b D 2 and show the following.
(a) The squared deviations .Ln.ij /LAn
.i/LBn
.j //2 do not depend on the choice of ij 2 E, so that eDn D Z2 n for
![]()
(b) Let XA k D 1 if the A-coordinate of Xk is equal to 1, set XA k D 0 otherwise, and define XB k similarly. Then, on the one hand, ![]()
and on the other hand
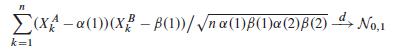
relative to each P˛˝ˇ in the null hypothesis. (Note that the family ¹XA k ;XB k W k 1º is independent under P˛˝ˇ .)
(c) Use Proposition (11.2) (in its one-dimensional version) to show that Zn !d N0;1 with respect to P˛˝ˇ , and therefore eDn !d 2 1 under the null hypothesis.
Zn = n (Ln(11) L^ (1) LB (1))/LA (1)LB (1)LA (2)LB (2).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


