Question: Consider the granulation model that was given in Example 23.2. (a) Design an MPC controller, using the nominal process model. Initially consider a control horizon
(a) Design an MPC controller, using the nominal process model. Initially consider a control horizon of M = 2 and a prediction horizon of P = 40 (with a sampling period of Δt = 1). Use equal weights on the manipulated inputs and penalize the two percentile outputs equally, but use a larger weight on the bulk density y1.
(b) Consider the effect of a plant-model mismatch. Use the problem statement for control design, but assume that the actual process is characterized by the following parameters:
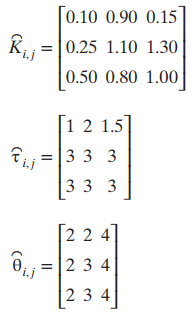
(c) These models are in deviation variables, but the actual steady-state flow rates for the nozzles are 175, 175, and 245, respectively. The steady-state outputs are 40, 400, and 1620, respectively. Nozzle flow rates are limited to values between 100 and 340, and it is desired to keep the 5th percentile (y2) above 350 and the 90th percentile y3 below 1650. Simulate the response of the controller to the following changes:
(i) Step change in bulk density from 40 to 90.
(ii) Simultaneous change in the 5th percentile from 400 to 375 and 90th percentile from 1620 to 1630. Comment on the performance of your controller (and retune as necessary).
[0.10 0.90 0.15 R.j K, =|0.25 1.10 1.30 0.50 0.80 1.00 [1 2 1.5 =|3 3 3 3 3 3 [2 2 4 =12 3 4 2 3 4
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (179 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Sample code for MPC design provided below b Sample code for MPC design provided below c Sa... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


