Question: Prove that the grammars in Figure C 2.37 lie in the regions claimed. Figure 2.37 LL(2) but not SLL: SLL(k) and SLR(k) but not LR(k
Prove that the grammars in Figure C 2.37 lie in the regions claimed.
Figure 2.37
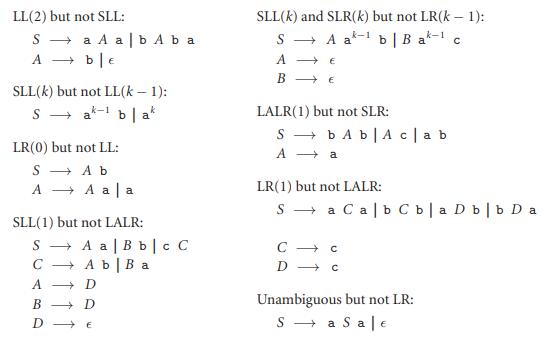
LL(2) but not SLL: SLL(k) and SLR(k) but not LR(k 1): S - A at- b | B a- c k-1 S a A a| b A b a A + be k-1 A E SLL(k) but not LL(k 1): S - a- b | a k-1 LALR(1) but not SLR: S - bA b|A c|ab A + a LR(0) but not LL: S + A b A + A a a LR(1) but not LALR: S - a Calb C b|a D b|b D a SLL(1) but not LALR: S - A a | B b |c C C - Ab| B a A Unambiguous but not LR: S - a Sa| B + D
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (173 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
LL2 but not SLL S a A a b A b a A b Recall that the difference between LL and SLL is local versus global follow sets Realized as a PDA an SLL parser has but two states one of which is used only to acc... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


