Question: ... . .. . . . . . . . . ....... A ray of light reflects off a spherical water drop and streams to
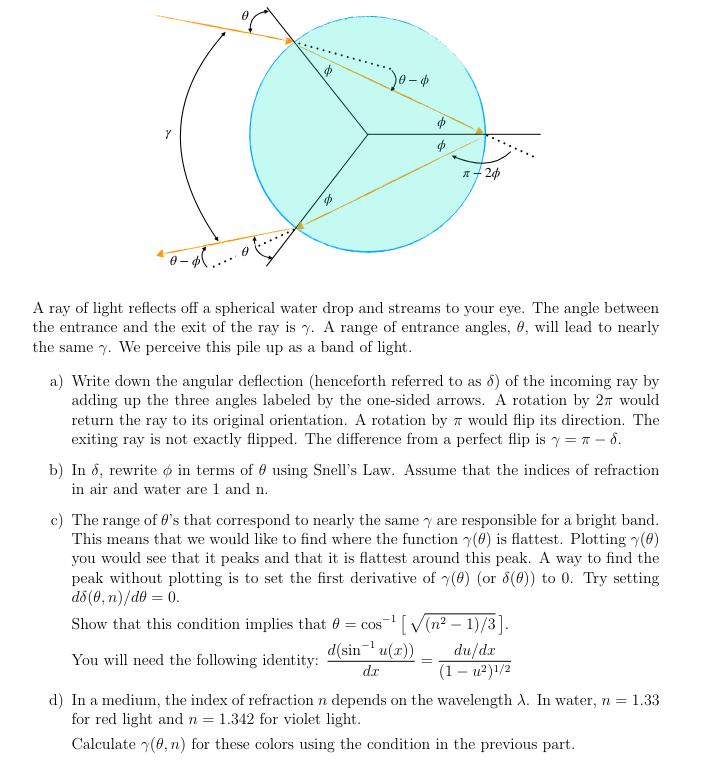
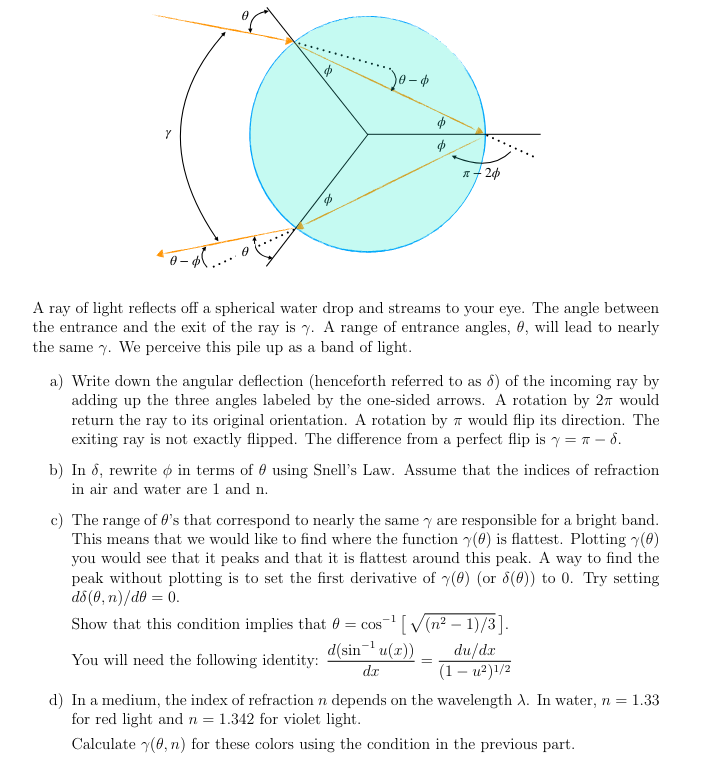
... . .. . . . . . . . . ....... A ray of light reflects off a spherical water drop and streams to your eye. The angle between the entrance and the exit of the ray is y. A range of entrance angles, 0, will lead to nearly the same y. We perceive this pile up as a band of light. a) Write down the angular deflection (henceforth referred to as 6) of the incoming ray by adding up the three angles labeled by the one-sided arrows. A rotation by 2x would return the ray to its original orientation. A rotation by a would flip its direction. The exiting ray is not exactly flipped. The difference from a perfect flip is y = * - 6. b) In 6, rewrite $ in terms of 0 using Snell's Law. Assume that the indices of refraction in air and water are 1 and n. c) The range of #'s that correspond to nearly the same y are responsible for a bright band. This means that we would like to find where the function y(0) is flattest. Plotting y(0) you would see that it peaks and that it is flattest around this peak. A way to find the peak without plotting is to set the first derivative of y(0) (or 6(0)) to 0. Try setting do (8, n)/de = 0. Show that this condition implies that o = cos ' [ v(n3 - 1)/3]. You will need the following identity: d(sinu(x)) du/dx (1 - 12)1/2 1) In a medium, the index of refraction n depends on the wavelength A. In water, n = 1.33 for red light and n = 1.342 for violet light. Calculate (0, n) for these colors using the condition in the previous part
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


