Question: 0 5. 5 Table 3 shows data about two electric bicycles. Table 3 Bicycle A Bicycle B Maximum distance between charges in kilometres 112 56
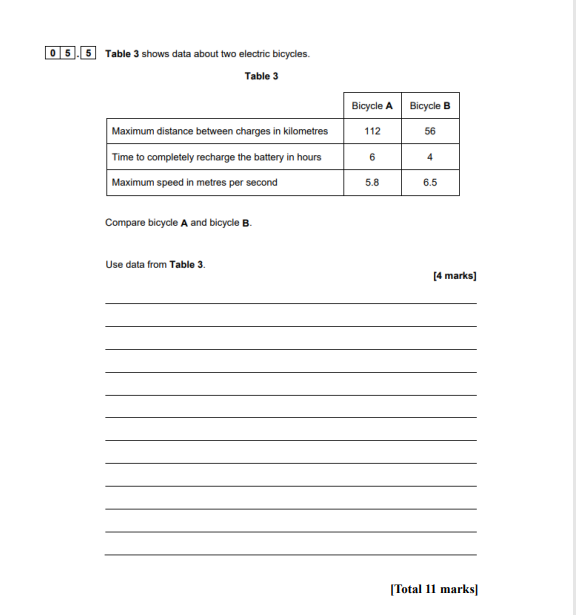

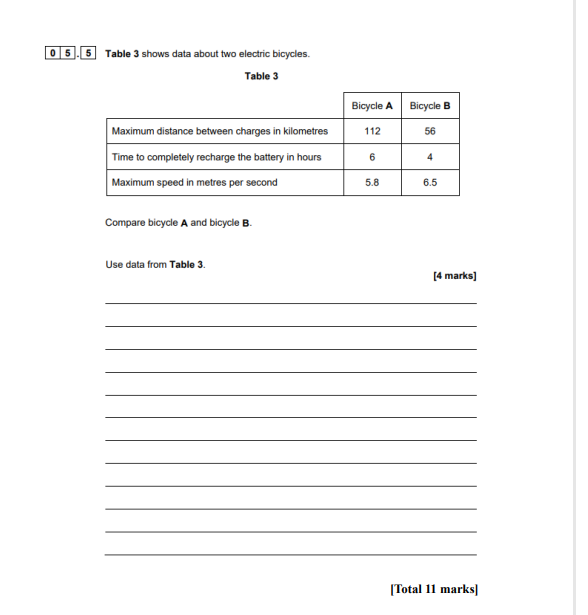

0 5. 5 Table 3 shows data about two electric bicycles. Table 3 Bicycle A Bicycle B Maximum distance between charges in kilometres 112 56 Time to completely recharge the battery in hours 6 Maximum speed in metres per second 5.8 6.5 Compare bicycle A and bicycle B. Use data from Table 3. [4 marks] [Total 11 marks]0 5 Figure 5 shows a cyclist riding an electric bicycle After 1200 seconds the cyclist becomes tired and switches on the motor. Figure 5 0 5. 3 The potential difference across the motor is 36 V. The current in the motor is 15 A. Calculate the power of the motor. Use the Physics Equations Sheet. [2 marks] Power Battery Motor Pedal The electric bicycle can be moved by the cyclist pushing on the pedals. 0 5.4 The power of the motor is constant. The cyclist can also switch on a motor to power the bicycle. Suggest one factor that could affect the speed of the bicycle after 1200 seconds. [1 mark] 0 5. 1 The cyclist travels a distance of 5400 m in 1200 seconds by pushing on the pedals. Calculate the average speed of the cyclist. Use the Physics Equations Sheet. [2 marks] Average speed = m/s 0 5. 2 The energy transferred by the cyclist is 540 000 J. Calculate the average power of the cyclist during the 1200 s. Use the Physics Equations Sheet. [2 marks] Average power =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


