Question: 0.02 Explain your answer. OHo : p = 0.02 versus Ha : p > 0.02 , as the conversion will only happen if the proportion
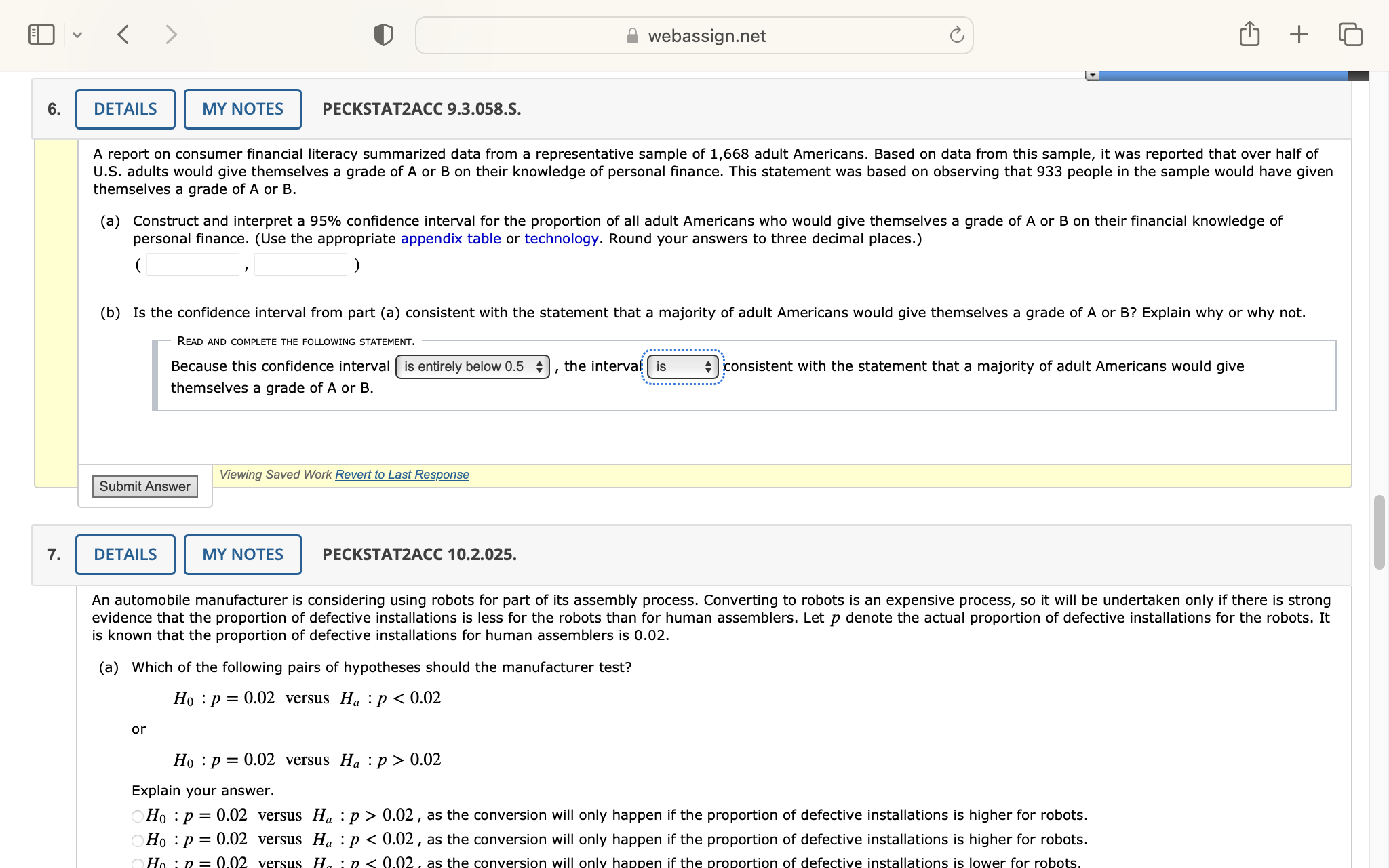
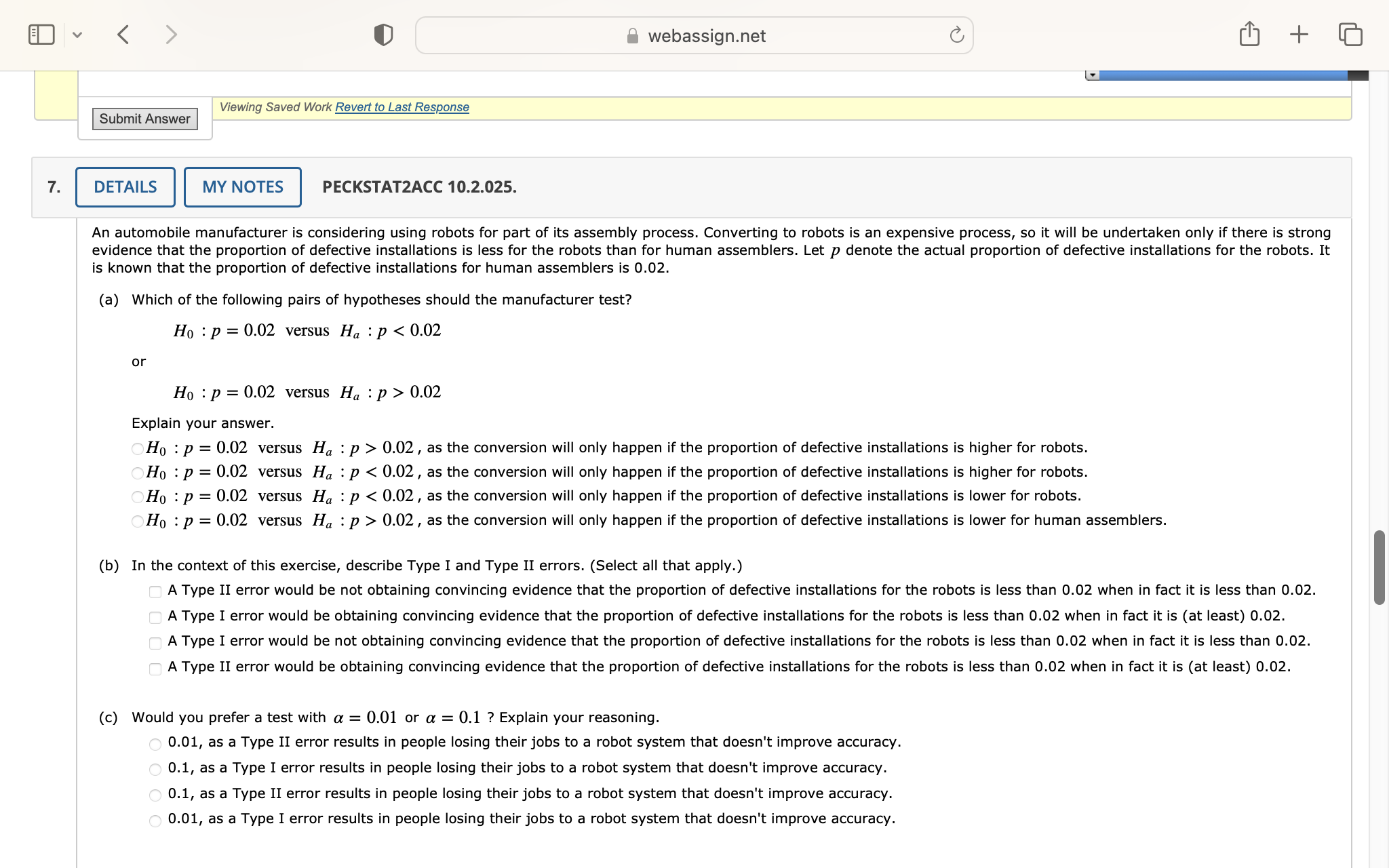
0.02 Explain your answer. OHo : p = 0.02 versus Ha : p > 0.02 , as the conversion will only happen if the proportion of defective installations is higher for robots. Ho : p = 0.02 versus Ha : p 0.02 Explain your answer. Hy : p=0.02 versus H, : p > 0.02, as the conversion will only happen if the proportion of defective installations is higher for robots. Hy : p=0.02 versus H, : p 0.02, as the conversion will only happen if the proportion of defective installations is lower for human assemblers. (b) 1In the context of this exercise, describe Type I and Type 1I errors. (Select all that apply.) A Type II error would be not obtaining convincing evidence that the proportion of defective installations for the robots is less than 0.02 when in fact it is less than 0.02. A Type I error would be obtaining convincing evidence that the proportion of defective installations for the robots is less than 0.02 when in fact it is (at least) 0.02. A Type I error would be not obtaining convincing evidence that the proportion of defective installations for the robots is less than 0.02 when in fact it is less than 0.02. A Type II error would be obtaining convincing evidence that the proportion of defective installations for the robots is less than 0.02 when in fact it is (at least) 0.02. (c) Would you prefer a test with @ = 0.01 or @ = 0.1 ? Explain your reasoning. 0.01, as a Type II error results in people losing their jobs to a robot system that doesn't improve accuracy. 0.1, as a Type I error results in people losing their jobs to a robot system that doesn't improve accuracy. 0.1, as a Type II error results in people losing their jobs to a robot system that doesn't improve accuracy. 0.01, as a Type I error results in people losing their jobs to a robot system that doesn't improve accuracy
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


