Question: 0.2 pts Question 10 Apply concepts from pages 6-1 through 6-4 and page 6-7 of the VLN to answer the following: The company sales were
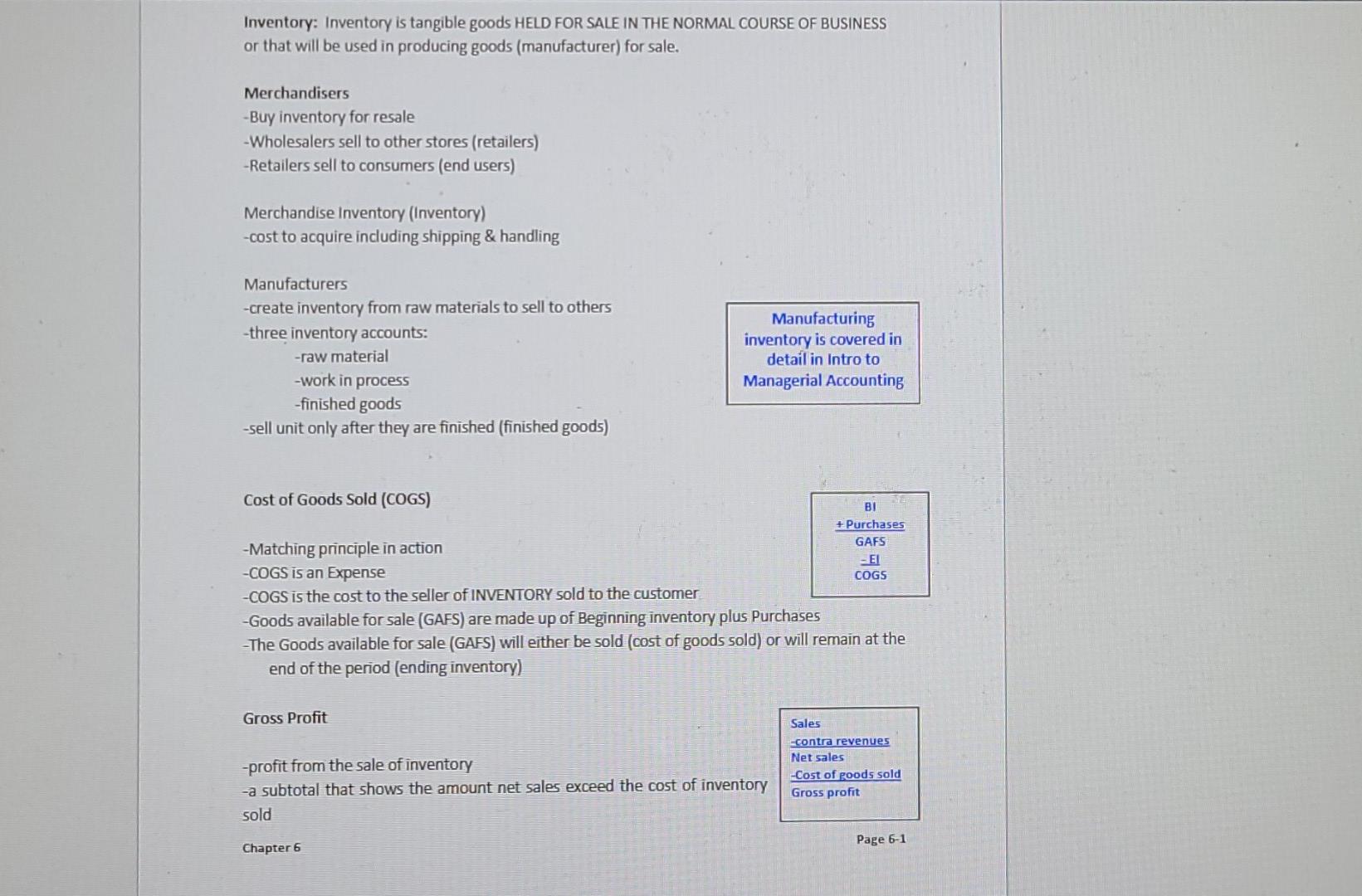
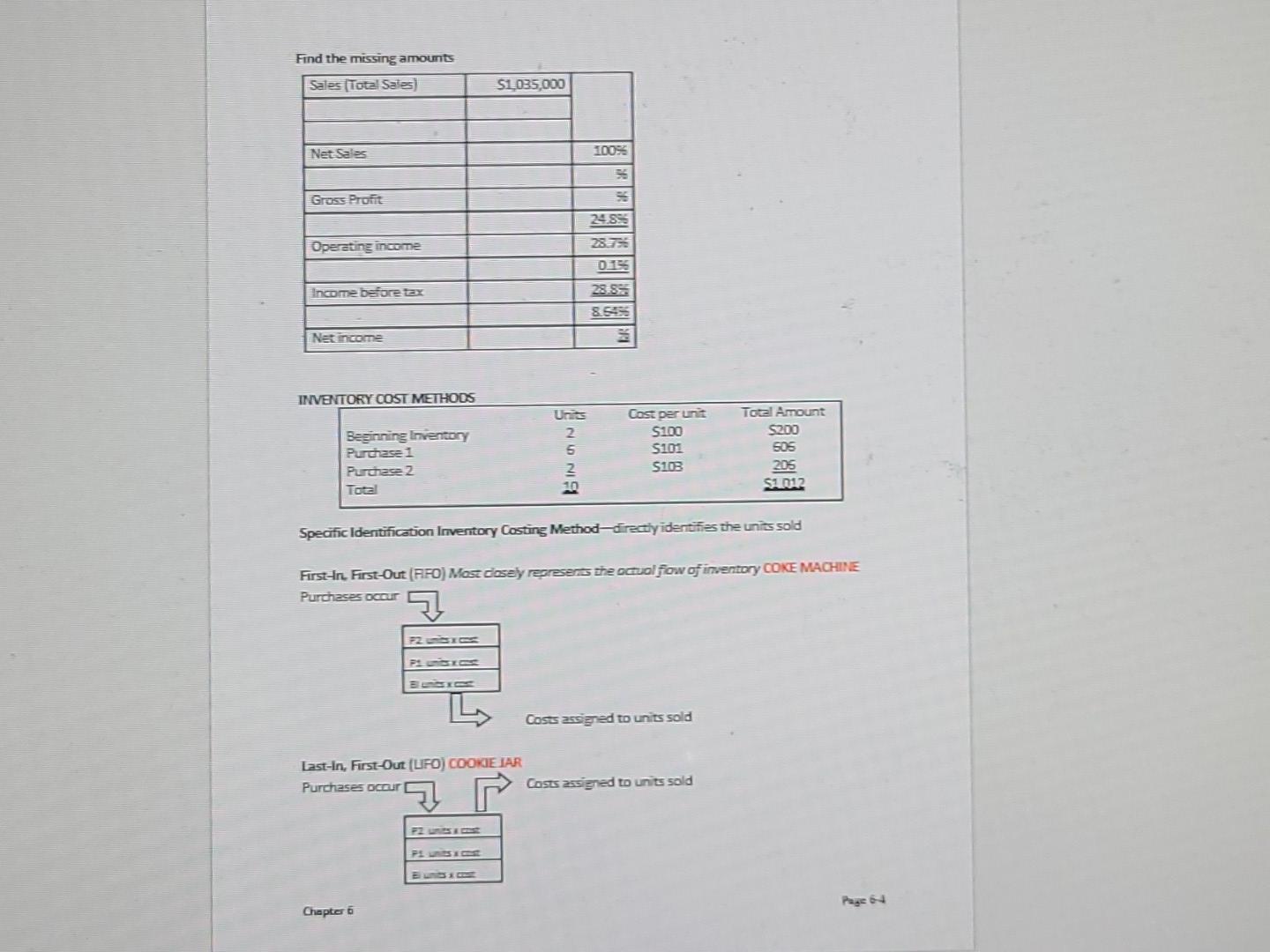
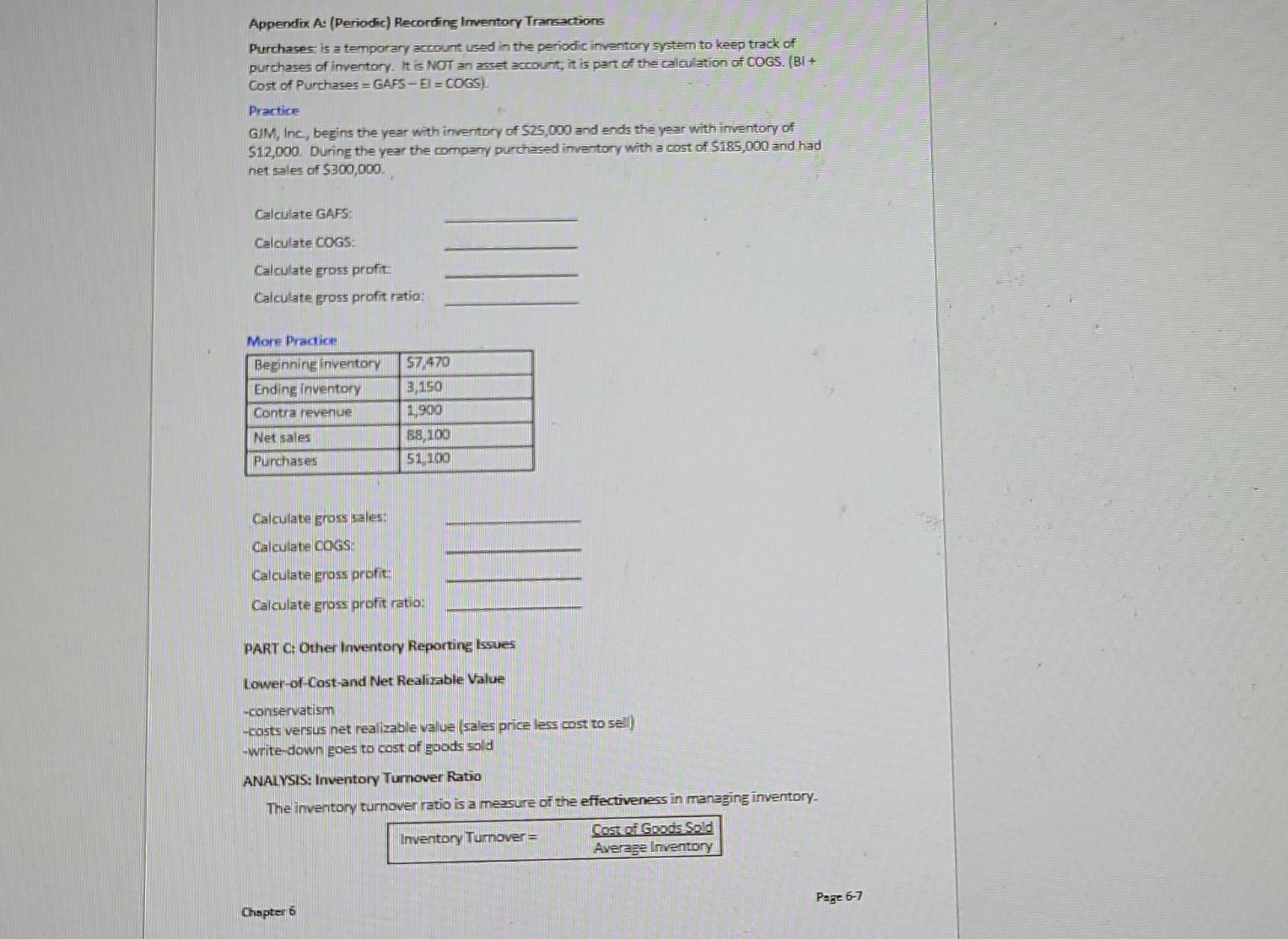
0.2 pts Question 10 Apply concepts from pages 6-1 through 6-4 and page 6-7 of the VLN to answer the following: The company sales were $500,000 they had $10,000 in sales discounts and cost of good sold of $320,000 and operating expenses totaling $120,000. What is the company's gross profit ratio? Carry it out to 1 decimal place. Do not include the % sign in your answer. ___._%. Inventory: Inventory is tangible goods HELD FOR SALE IN THE NORMAL COURSE OF BUSINESS or that will be used in producing goods (manufacturer) for sale. Merchandisers -Buy inventory for resale -Wholesalers sell to other stores (retailers) -Retailers sell to consumers (end users) Merchandise Inventory (Inventory) -cost to acquire including shipping & handling Manufacturers -create inventory from raw materials to sell to others --three inventory accounts: -raw material -work in process -finished goods -sell unit only after they are finished (finished goods) Manufacturing inventory is covered in detail in Intro to Managerial Accounting Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) BI + Purchases -Matching principle in action GAFS EL -COGS is an Expense COGS -COGS is the cost to the seller of INVENTORY sold to the customer -Goods available for sale (GAFS) are made up of Beginning inventory plus Purchases -The Goods available for sale (GAFS) will either be sold (cost of goods sold) or will remain at the end of the period (ending inventory) Gross Profit -profit from the sale of inventory -a subtotal that shows the amount net sales exceed the cost of inventory sold Sales contra revenues Net sales -Cost of goods sold Gross profit Page 6-1 Chapter 6 Find the missing amounts Sales Total Sales) $1.035,000 Net Sales 10096 Gross Profit Operating income 24.99 2875 011 28.53 8.59 Income before tax Net income INVENTORY COST METHODS Units Beginning Inventory Purchase 1 Purchase 2 Total NANI Cost perunt S100 S101 $105 Total Amount 5200 505 205 S2012 10 Specific Identification Inventory Costing Method - directly identifies the units sold First-In First-Out (FFO) Most Cosey reareSens the occuolfow of inventory COKE MACHINE Purchases occur 72 Costs assigned to units sold Last-In, First-Out (LFO) COOKIE JAR Purchases ocuri Costs assigned to units sold 2 PLUS Chapter 6 Appendix A: (Periodic) Recording Inventory Transactions Purchases is a temporary account used in the periodic inventory system to keep track of purchases of inventory. It is NOT an asset account, it is part of the calculation of COGS. (BI+ Cost of Purchases = GAFS-El=COGS) Practice GIM, Inc., begins the year with inventory of $25,000 and ends the year with inventory of $12,000. During the year the company purchased inventory with a cost of $185,000 and had net sales of $300,000 Calculate GAPS Calculate COGS Calculate Eross profit Calculate gross profit ratio: More Practice Beginning inventory Ending inventory Contra revenue Net sales Purchases $7,470 3,150 1900 88,100 51100 Calculate gross sales: Calculate COGS Calculate gross profit: Calculate gross profit ratio: PART 2: Other Inventory Reporting Issues Lower-of-Cast and Net Realizable Value -conservatism -costs versus net realizable value (sales price less cost to sell) -write-down goes to cost of goods sold ANALYSIS: Inventory Turnover Ratio The inventory turnover ratio is a measure of the effectiveness in managing inventory. Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold Average Inventory Page 6-7 Chapter 6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


