Question: ( 1 0 0 points ) Assume that the pressure ratio R p = P 2 P 1 across the compressor of an ideal thermodynamic
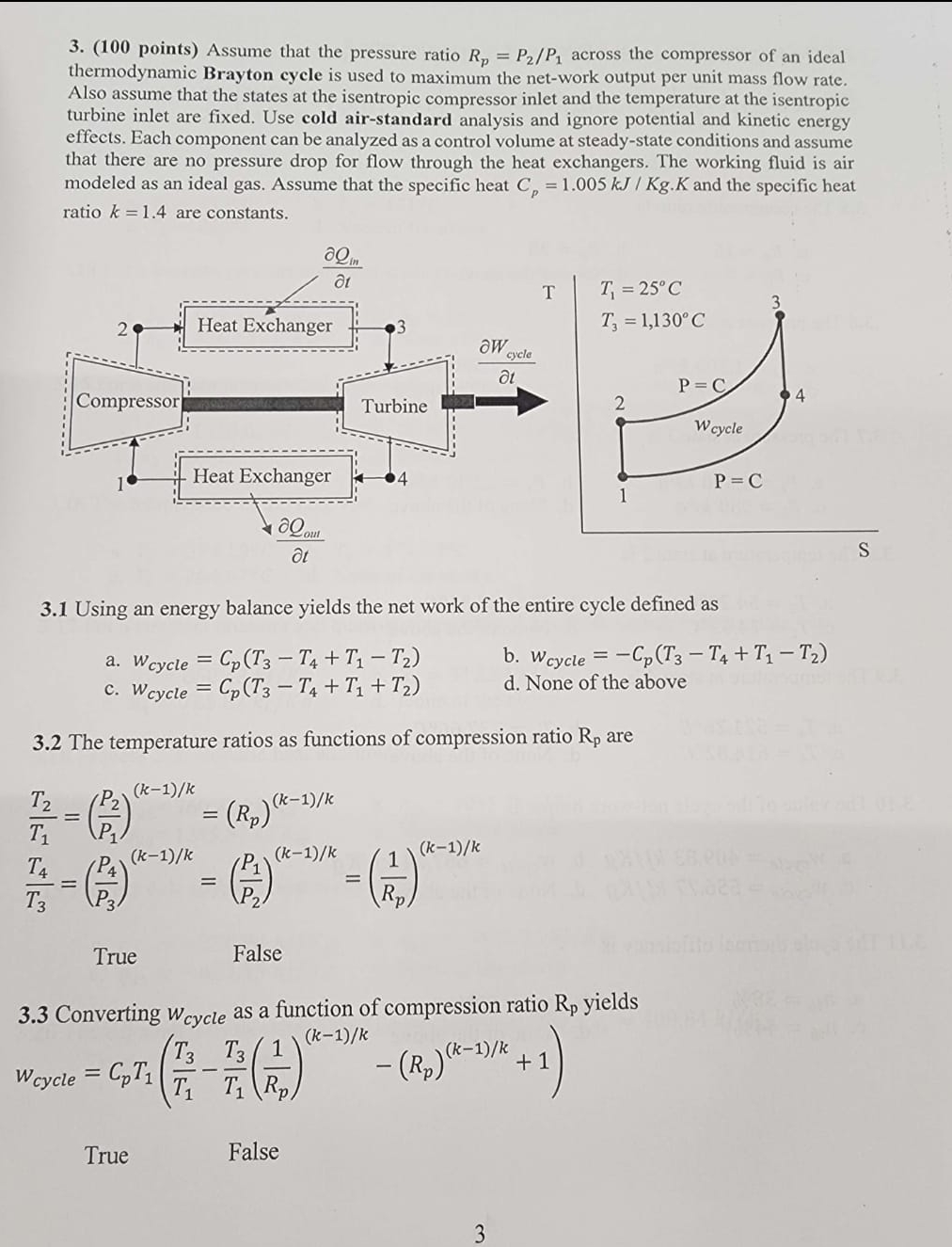
points Assume that the pressure ratio across the compressor of an ideal thermodynamic Brayton cycle is used to maximum the network output per unit mass flow rate. Also assume that the states at the isentropic compressor inlet and the temperature at the isentropic turbine inlet are fixed. Use cold airstandard analysis and ignore potential and kinetic energy effects. Each component can be analyzed as a control volume at steadystate conditions and assume that there are no pressure drop for flow through the heat exchangers. The working fluid is air modeled as an ideal gas. Assume that the specific heat and the specific heat ratio are constants.
Using an energy balance yields the net work of the entire cycle defined as
a
b
c
d None of the above
The temperature ratios as functions of compression ratio are
True False
Converting as a function of compression ratio yields
True
False
The derivative of as a function of compression ratio is
True
False
The compression ratio is
a
b
c
d None of the above
The pressure at state is
akPa
bkPa
ckPa
d None of the above
The pressure at state is
akPa
bkPa
ckPa
d None of the above
The temperature at state is
a
b
c
d None of the above
The temperature at state is
a
b
c
d None of the above
The value of the cycle network output is
a
b
c
d None of the above
The cycle thermal efficiency is
a
b
c
d None of the above
For a constant pressure and quasistatic process, the specific enthalpy of state is
a
c
b
d None of the above
The temperature of the state is
a
c
b
d None of the above
For a constant pressure and quasistatic process, the specific enthalpy of state is
a
c
b
d None of the above
For a constant pressure and quasistatic process, the specific enthalpy of the state is
a
b
c
d None of the above
The temperature of the state is
a
b
c
d None of the above
For a constant pressure and quasistatic process, the specific enthalpy of the state is
a
b
c
ALL QUESTIONS PLIZ
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


