Question: 1 2 3 4 5 6 4 7 import java.io.File; 8 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 9 import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 5 6 8 9 0 8
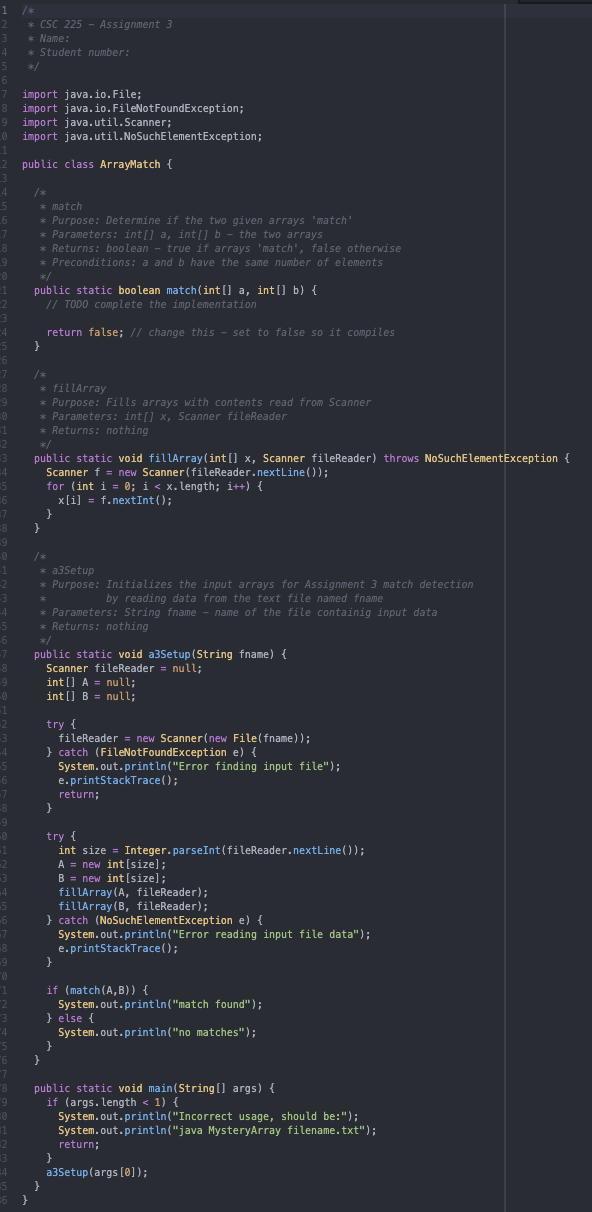

1 2 3 4 5 6 4 7 import java.io.File; 8 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 9 import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 5 6 8 9 0 8 19 0 :7 8 3 -4 -5 4 i0 51 2 3 4 6 "4 * CSC 225 - Assignment 3 * Name: #6 * Student number: */ public class ArrayMatch { * match * Purpose: Determine if the two given arrays 'match' * Parameters: int[] a, int[] b - the two arrays * Returns: boolean - true if arrays 'match', false otherwise * Preconditions: a and b have the same number of elements */ public static boolean match(int[] a, int[] b) { // TODO complete the implementation return false; // change this set to false so it compiles } * fillArray * Purpose: Fills arrays with contents read from Scanner * Parameters: int[] x, Scanner fileReader * Returns: nothing */ public static void fillArray (int[] x, Scanner fileReader) throws NoSuchElementException { Scanner f = new Scanner (fileReader.nextLine()); for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) { x[i] = f.nextInt(); } } * a3Setup * Purpose: Initializes the input arrays for Assignment 3 match detection by reading data from the text file named fname * Parameters: String fname - name of the file containig input data * Returns: nothing */ public static void a3Setup (String fname) { Scanner fileReader = null; int[] A = null; int[] B = null; } try { fileReader = new Scanner(new File(fname)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("Error finding input file"); e.printStackTrace(); return; } try { int size= Integer.parseInt(fileReader.nextLine()); A = new int[size]; B = new int[size]; fillArray (A, fileReader); fillArray (B, fileReader); } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { System.out.println("Error reading input file data"); e.printStackTrace(); } } if (match (A,B)) { System.out.println("match found"); } else { System.out.println("no matches"); public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length < 1) { System.out.println("Incorrect usage, should be:"); System.out.println("java MysteryArray filename.txt"); return; } a3Setup (args[0]); 3. Complete the implementation of the match method in ArrayMatch.java. This method determines if a match (something we are defining for this particular problem) can be found when examining two arrays, A and B. B. and B are arrays of size n, containing the same number of integer elements. Two arrays, A and B, are defined to be matches of one another if at least one of the following two conditions is satisfied: I. A=B (the arrays have the same elements at each index) II. If n is divisible by 2, A and B are divided into two sub-arrays of equal size (A is divided into A and A, B into B and B). Then, at least one of the following conditions is satisfied: a) (A matches B)^(Amatches B) b) (A matches B)^(Amatches B) c) (Amatches B)^(Amatches B) Note: if n is not divisible by 2, condition II is not satisfied. Additional Information: You cannot change the method signature for match at all (two integer arrays as parameters, and returns a boolean) or you will receive a score of 0. If your submission fails to compile, you will receive a score of 0. You are welcome to create additional methods to aid in your implementation, but again, the match method must return a boolean when given two integer arrays. The methods provided for you will handle file I/O. When executed, the program reads from input files, and outputs whether a match is found based on the array data found in the file. The program is executed in the following way: java ArrayMatch filename.txt Input files must be three lines, formatted in the following way: You have been provided with some sample files. It is strongly recommended you add further tests. File name test01.txt test02.txt test03.txt test04.txt Expected output match found no matches match found match found Reasoning A=B AB, and no conditions from II are satisfied: when the arrays are split, AB, A B A #B, and A B, and the size (n) is not divisible by 2 for these arrays, so no further splits are made. II b) is satisfied, (A matches B)^(Amatches B) II a) is satisfied: (A matches B) trivially. Eventually we will also see A matches B after a number of sub-arrays are created and determined to be matches of one another. I recommend drawing a picture!
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


