Question: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. In the MIPS processor pipeline, the context associated with the
1.
 2.
2.
 3.
3.
 4.
4.
 5.
5.
 6.
6.
 7.
7.
8.

9.
 10.
10.
 11.
11.
 12.
12.
 13.
13.
 14.
14.
 15.
15.

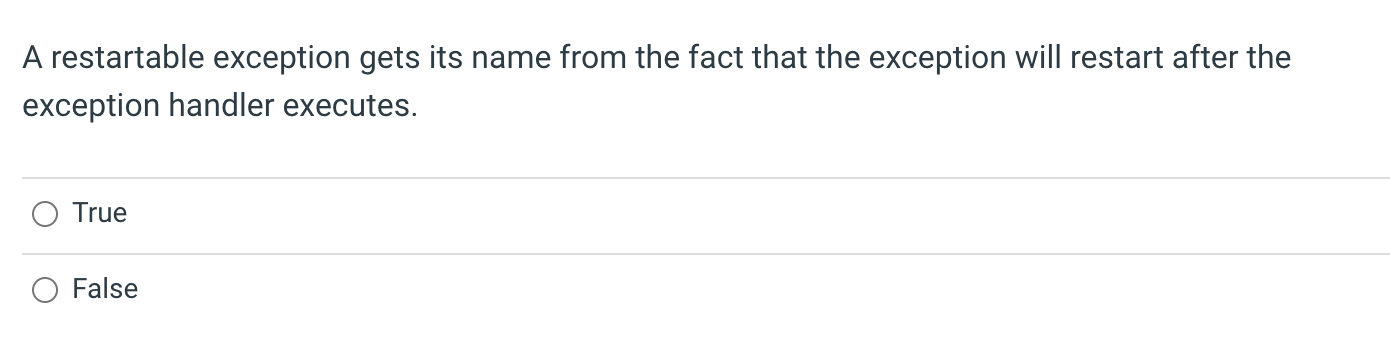
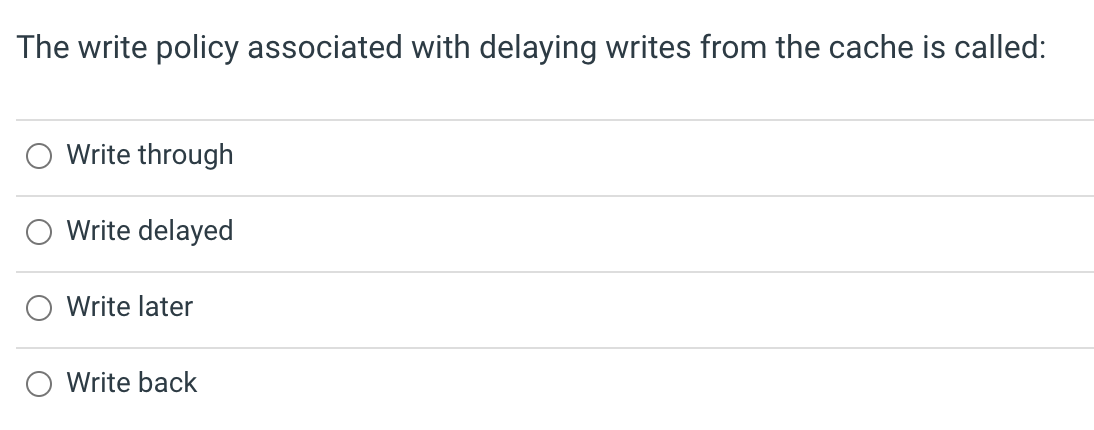
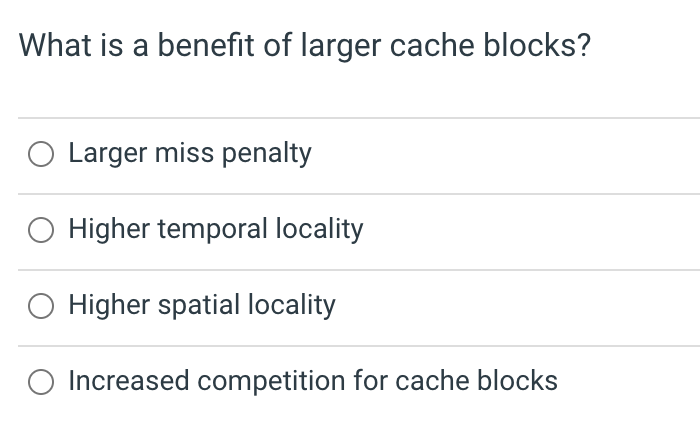
In the MIPS processor pipeline, the context associated with the newest instruction can be found in which pipeline register? IF/ID ID/EX EX/MEM MEM/WB A restartable exception gets its name from the fact that the exception will restart after the exception handler executes. True False Which is not a potential benefit of the Harvard machine architecture? Appealing aesthetic (brick and mortar) Eliminating structure hazards Tuning instruction memory performance separate from data memory Read-only instruction memory vs read/write data memory Processor caches typically store some of the bytes surrounding the requested information. This will improve performance through the principle of: Spatial Locality Temporal Locality Both Spatial and Temporal Locality Neither Spatial nor Temporal Locality The cache block status bit associated with the write-back write policy is: valid dirty present written The write policy associated with delaying writes from the cache is called: Write through Write delayed Write later Write back What is a benefit of larger cache blocks? Larger miss penalty Higher temporal locality Higher spatial locality Increased competition for cache blocks Conflict misses are due to First access to a block Limited cache size Competition for entries in a set Write policy What will the hit rate of the "cachebuster" algorithm be if the array size is 4x the cache size and the stride is half the block width 0% 50%100%200% Grouping variables that are used together into a common structure can improve cache performance by: Increasing miss rates Increasing temporal locality Increasing spatial locality Reducing the overall data used by the program Variables in an array that are accessed frequently and sequentially display: Spatial Locality Temporal Locality Both Spatial and Temporal Locality Neither Spatial nor Temporal Locality Which of the following is not likely to reduce the number of page faults? Reducing the software load on the system Increasing the amount of system memory Using a smart replacement algorithm Increase the amount of disk space In the memory hierarchy, memories that are farther from the CPU will be characterized by Higher speed All of these characteristics Higher cost per byte Higher capacity In the memory hierarchy, memories that are farther from the CPU will be characterized by Lower speed All of these characteristics Lower cost per byte Higher capacity In the memory hierarchy, memories that are farther from the CPU will be characterized by Lower speed All of these characteristics Higher cost per byte Smaller capacity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


