Question: 1 2 . Go back to the future _ value.py file. Then, comment out the get _ number and get _ integer ( ) functions.
Go back to the futurevalue.py file. Then, comment out the getnumber and getinteger functions.
Add an import statement that imports the validation module.
Modify the code in the main function so it uses the functions in the validation module
When you completed modifications shown above, then enhance your program so the console will look something like this:
Financial Calculator Options
Future Value Calculation
Simple Interest Calculation
Quit
Choose an option :
monthly investment:
Entry must be greater than and less than or equal to
Enter monthly investment:
Enter yearly interest rate:
Entry must be greater than and less than or equal to
Enter yearly interest rate:
Enter number of years:
Entry must be greater than and less than or equal to
Enter number of years:
Future Value
Financial Calculator Options
Future Value Calculation
Simple Interest Calculation
Quit
Choose an option :
Enter principal amount:
Entry must be greater than and less than or equal to
Enter principal amount:
Enter annual interest rate:
Entry must be greater than and less than or equal to
Enter annual interest rate:
Enter time period in years:
Entry must be greater than and less than or equal to
Enter time period in years:
Simple Interest:
Financial Calculator Options
Future Value Calculation
Simple Interest Calculation
Quit
Choose an option :
Goodbye!
The new enhancement is Adding a Menu for Multiple Options
Display Menu: A function displaymenu is created to show the user the available options eg Future Value Calculation", Simple Interest Calculation", Quit"
Main Loop for Menu: The main function contains a while loop that runs indefinitely until the user chooses to quit by selecting option
Based on the users input, the program uses conditional checks ifelifelse to decide which operation to perform.
Simple Interest Calculation: Prompts for principal, interest rate, and time years then computes simple interest as this:
simpleinterest principal interestrate years where principal, interestrate and years are user input values
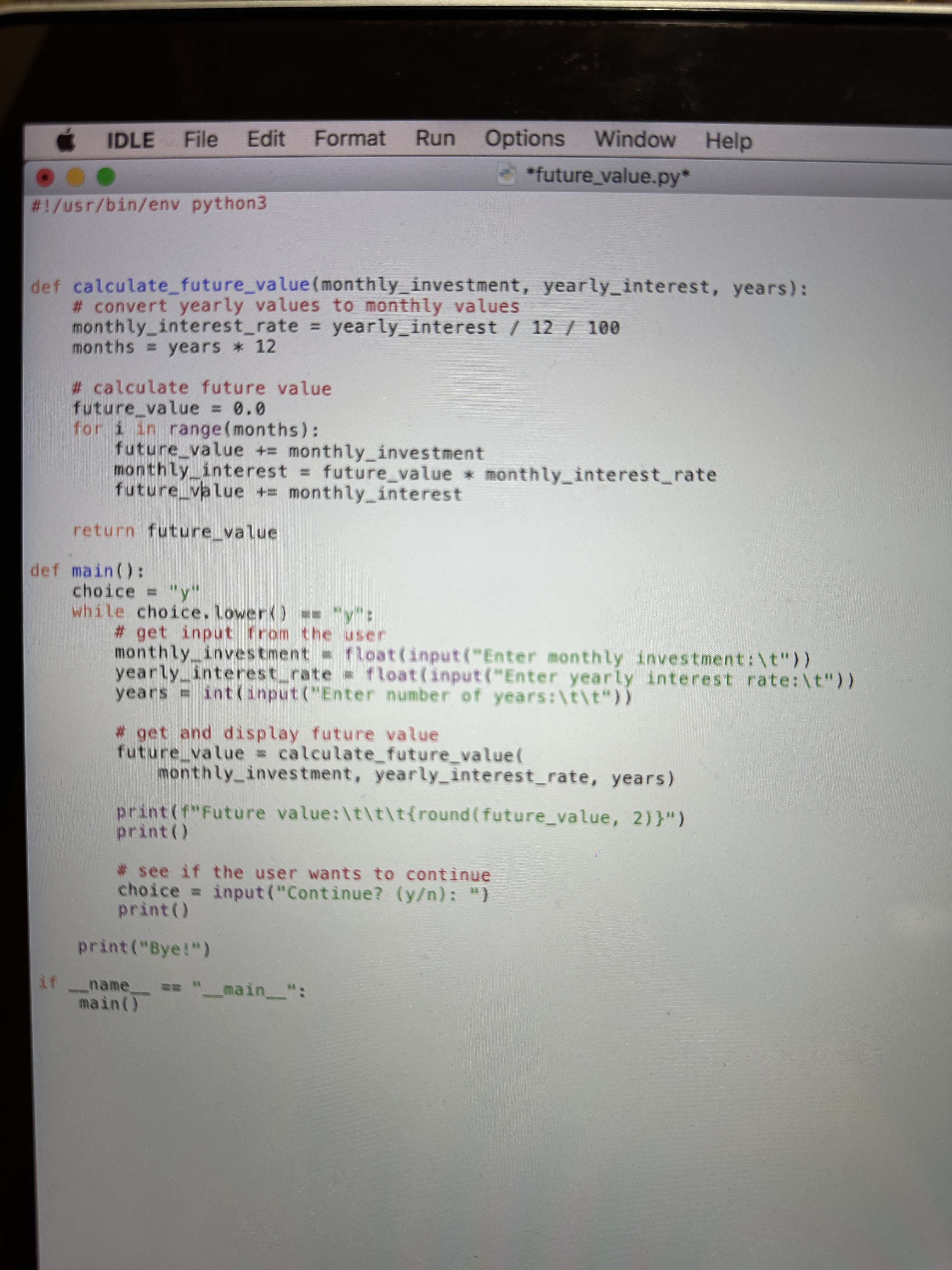
def calculatefuturevaluemonthlyinvestment, yearlyinterest, years:
# convert yearly values to monthly values
monthlyinterestrate yearlyinterest
months years
# calculate future value
futurevalue
for i in rangemonths:
futurevalue monthlyinvestment
monthlyinterest futurevalue monthlyinterestrate
futurevalue monthlyinterest
return futurevalue
def main:
choice y
while choice.lowery:
# get input from the user
monthlyinvestment floatinputEnter monthly investment:t
yearlyinterestrate floatinputEnter yearly interest rate:t
years intinputEnter number of years:tt
## get and display future value
futurevalue calculatefuturevalue
monthlyinvestment, yearlyinterestrate, years
printfFuture value:tttroundfuturevalue,
print
see if the user wants to continue
choice inputContinueyn:
print
printye
operatornamemain main :
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


