Question: 1. 2. - X Data Table Per Pair Requirements 1. Asad produces Standard and Deluxe sunglasses: Click the icon to view the cost data.) Click
1.
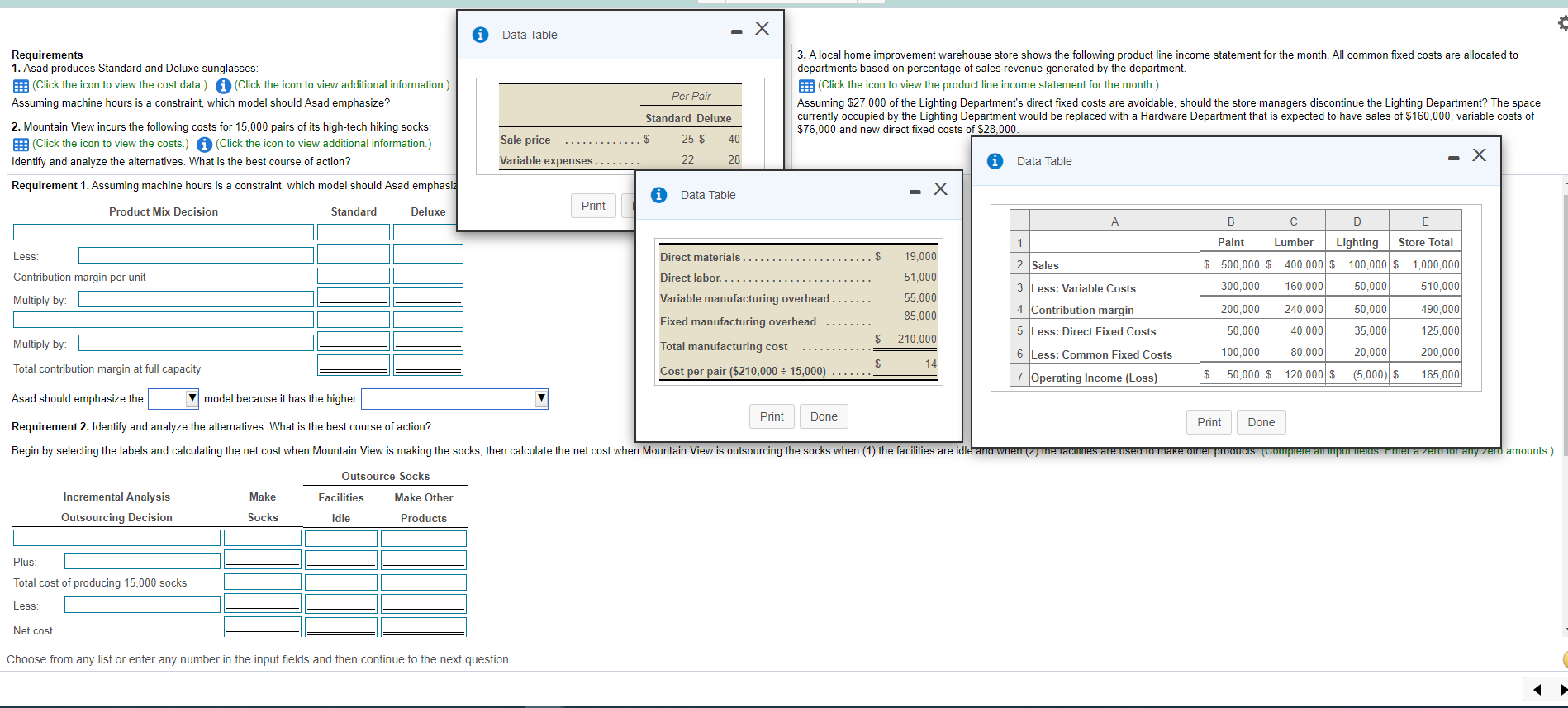
2.
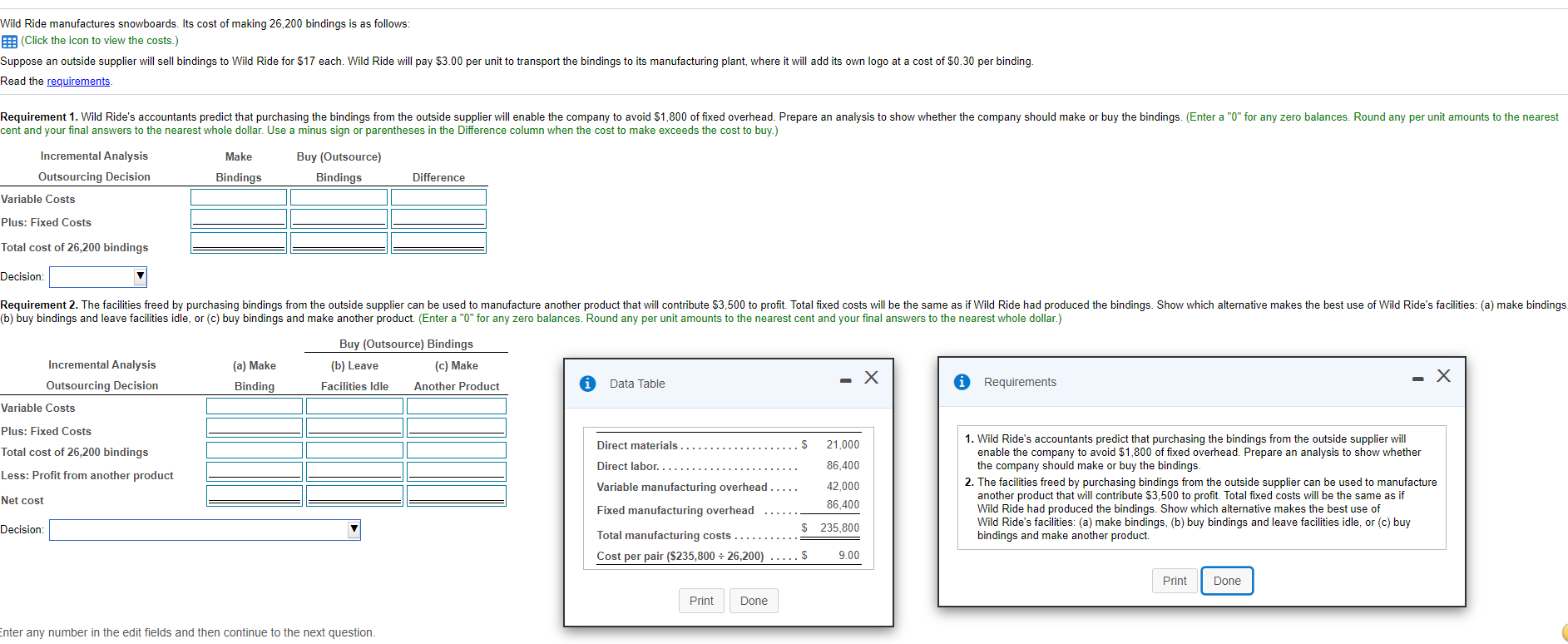
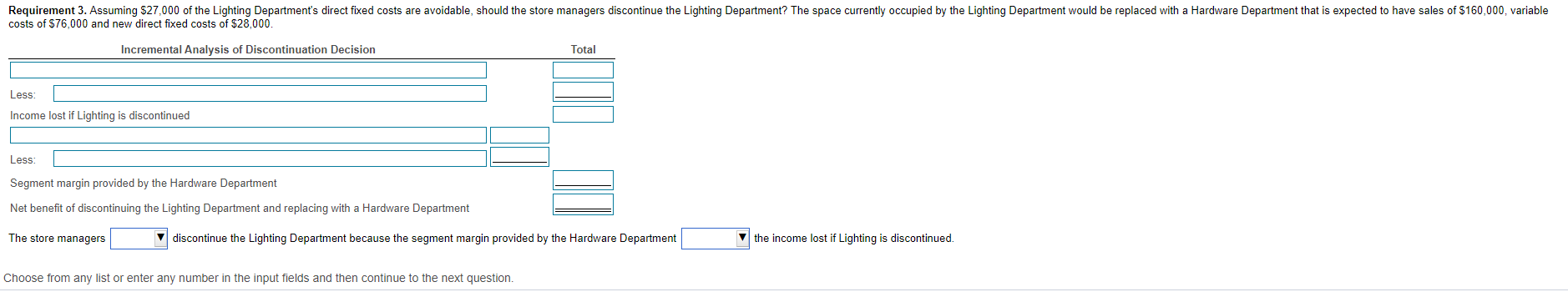
- X Data Table Per Pair Requirements 1. Asad produces Standard and Deluxe sunglasses: Click the icon to view the cost data.) Click the icon to view additional information.) Assuming machine hours is a constraint, which model should Asad emphasize? 2. Mountain View incurs the following costs for 15,000 pairs of its high-tech hiking socks: E: (Click the icon to view the costs.) (Click the icon to view additional information.) Identify and analyze the alternatives. What is the best course of action? Requirement 1. Assuming machine hours is a constraint, which model should Asad emphasi: 3. A local home improvement warehouse store shows the following product line income statement for the month. All common fixed costs are allocated to departments based on percentage of sales revenue generated by the department. (Click the icon to view the product line income statement for the month.) Assuming $27,000 of the Lighting Department's direct fixed costs are avoidable, should the store managers discontinue the Lighting Department? The space currently occupied by the Lighting Department would be replaced with a Hardware Department that is expected to have sales of $160,000, variable costs of $76,000 and new direct fixed costs of $28,000. Standard Deluxe Sale price 40 25 $ 22 Variable expenses........ 28 - X Data Table Data Table - X Print Product Mix Decision Standard Deluxe B D E 1 Paint Lumber Lighting Store Total Less Direct materials. $ 19,000 2 Sales $ 500,000 $ 400,000 $ 100,000 $ 1,000,000 Contribution margin per unit Direct labor. 51,000 3 Less: Variable Costs 300,000 160.000 50,000 510,000 Multiply by: Variable manufacturing overhead.... 55,000 4 Contribution margin 85.000 200,000 240,000 50,000 490,000 Fixed manufacturing overhead 5 Less: Direct Fixed Costs 50,000 40,000 35,000 125,000 $ 210,000 Multiply by: Total manufacturing cost 6 Less: Common Fixed Costs 100,000 80.000 20,000 200,000 $ 14 Total contribution margin at full capacity Cost per pair ($210,000 = 15,000) ....... 7 Operating Income (Loss) $ 50,000 $ 120,000 $ (5,000) $ 165,000 Asad should emphasize the model because it has the higher Print Done Requirement 2. Identify and analyze the alternatives. What is the best course of action? Print Done Begin by selecting the labels and calculating the net cost when Mountain View is making the socks, then calculate the net cost when Mountain View is outsourcing the socks when (1) the facilities are idle and when (2) the facilities are used to make other products. (Complete an impur Telds. Enter a zero for any zero amounts.) Outsource Socks Incremental Analysis Make Facilities Make Other Outsourcing Decision Socks Idle Products Plus: Total cost of producing 15,000 socks Less Net cost Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then continue to the next question. Requirement 3. Assuming $27,000 of the Lighting Department's direct fixed costs are avoidable, should the store managers discontinue the Lighting Department? The space currently occupied by the Lighting Department would be replaced with a Hardware Department that is expected to have sales of $160,000, variable costs of $76,000 and new direct fixed costs of $28,000. Incremental Analysis of Discontinuation Decision Total Less Income lost if Lighting is discontinued Less: Segment margin provided by the Hardware Department Net benefit of discontinuing the Lighting Department and replacing with a Hardware Department The store managers discontinue the Lighting Department because the segment margin provided by the Hardware Department the income lost if Lighting is discontinued. Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then continue to the next question. Wild Ride manufactures snowboards. Its cost of making 26,200 bindings is as follows: (Click the icon to view the costs.) Suppose an outside supplier will sell bindings to Wild Ride for $17 each. Wild Ride will pay $3.00 per unit to transport the bindings to its manufacturing plant, where it will add its own logo at a cost of $0.30 per binding. Read the requirements Requirement 1. Wild Ride's accountants predict that purchasing the bindings from the outside supplier will enable the company to avoid $1,800 of fixed overhead. Prepare an analysis to show whether the company should make or buy the bindings. (Enter a "0" for any zero balances. Round any per unit amounts to the nearest cent and your final answers to the nearest whole dollar. Use a minus sign or parentheses in the Difference column when the cost to make exceeds the cost to buy.) Make Incremental Analysis Outsourcing Decision Buy (Outsource) Bindings Bindings Difference Variable Costs Plus: Fixed Costs Total cost of 26,200 bindings Decision: Requirement 2. The facilities freed by purchasing bindings from the outside supplier can be used to manufacture another product that will contribute $3,500 to profit. Total fixed costs will be the same as if Wild Ride had produced the bindings. Show which alternative makes the best use of Wild Ride's facilities: (a) make bindings (b) buy bindings and leave facilities idle, or (C) buy bindings and make another product. (Enter a "0" for any zero balances. Round any per unit amounts to the nearest cent and your final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) (a) Make Buy (Outsource) Bindings (b) Leave (c) Make Facilities Idle Another Product Incremental Analysis Outsourcing Decision Variable Costs x - X Binding Data Table Requirements Plus: Fixed Costs Total cost of 26,200 bindings Less: Profit from another product Net cost Direct materials $ 21,000 Direct labor... 86,400 Variable manufacturing overhead ..... 42,000 86,400 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 235,800 Total manufacturing costs Cost per pair ($235,800 = 26,200) $ 9.00 1. Wild Ride's accountants predict that purchasing the bindings from the outside supplier will enable the company to avoid $1,800 of fixed overhead. Prepare an analysis to show whether the company should make or buy the bindings. 2. The facilities freed by purchasing bindings from the outside supplier can be used to manufacture another product that will contribute $3,500 to profit. Total fixed costs will be the same as if Wild Ride had produced the bindings. Show which alternative makes the best use of Wild Ride's facilities: (a) make bindings, (b) buy bindings and leave facilities idle, or (c) buy bindings and make another product. Decision: Print Done Print Done Enter any number in the edit fields and then continue to the next
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


