Question: 1 4 : 3 5 Sat 2 3 Nov 9 2 % MEE 2 1 2 Computer Project Particle 1 is confined within a smooth,
: Sat Nov
MEE
Computer Project
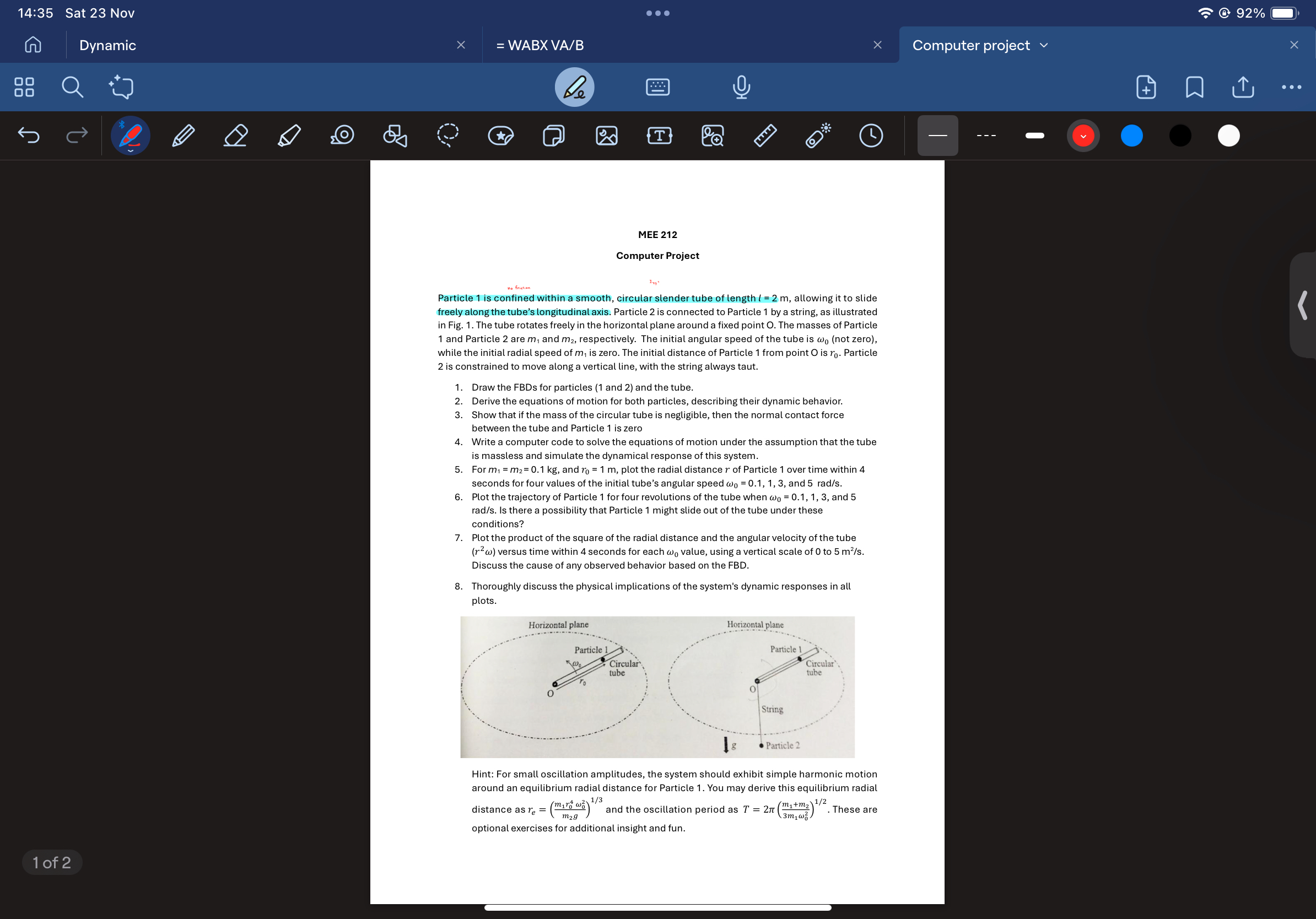
Particle is confined within a smooth, circular slender tube of length allowing it to slide freely along the tube's longitudinal axis. Particle is connected to Particle by a string, as illustrated in Fig. The tube rotates freely in the horizontal plane around a fixed point O The masses of Particle and Particle are and respectively. The initial angular speed of the tube is not zero while the initial radial speed of is zero. The initial distance of Particle from point O is Particle is constrained to move along a vertical line, with the string always taut.
Draw the FBDs for particles and and the tube.
Derive the equations of motion for both particles, describing their dynamic behavior.
Show that if the mass of the circular tube is negligible, then the normal contact force between the tube and Particle is zero
Write a computer code to solve the equations of motion under the assumption that the tube is massless and simulate the dynamical response of this system.
For and plot the radial distance of Particle over time within seconds for four values of the initial tube's angular speed and
Plot the trajectory of Particle for four revolutions of the tube when and Is there a possibility that Particle might slide out of the tube under these conditions?
Plot the product of the square of the radial distance and the angular velocity of the tube versus time within seconds for each value, using a vertical scale of to Discuss the cause of any observed behavior based on the FBD
Thoroughly discuss the physical implications of the system's dynamic responses in all plots.
Hint: For small oscillation amplitudes, the system should exhibit simple harmonic motion around an equilibrium radial distance for Particle You may derive this equilibrium radial distance as and the oscillation period as These are optional exercises for additional insight and fun.
of
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


