Question: 1. (5 points) Consider a passband signal whose in-phase part is a rectangle of unit height and duration 1 second, while the quadrature part is

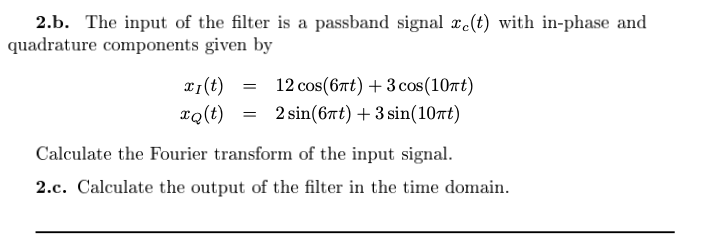
1. (5 points) Consider a passband signal whose in-phase part is a rectangle of unit height and duration 1 second, while the quadrature part is a rectangle of height equal to 2 and duration 2 seconds (both starting from time zero). The carrier frequency is 20 Hz. 1.a. Plot the passband signal in the time domain using MATLAB: Ts=...; %sampling period t=[0:Ts: 100); fc=20; %carrier frequency xi=... ; %in-phase signal xq=... ; %quadrature signal xz=xi+j*xq; %complex envelope xc=sqrt(2) *real(...); %passband signal (you can also use the formula with cosine and sine) tzoom=[0: Ts:3]; %reduced time axis for plotting in the time domain ltzoom=length(tzoom); plot(tzoom, xc(1:ltzoom)); 1.b. Calculate the Fourier transform of the passband signal using MATLAB. N=...; f=...; Xc=...; 1.c. Plot real and imaginary parts of the Fourier transform of the passband signal using MATLAB. 1.d. Using MATLAB, calculate the Fourier transform of the complex enve- lope. 1.e. Plot real and imaginary parts of the Fourier transform of the complex envelope using MATLAB. 1.f. Which of the above Fourier transforms satisfy Hermitian symmetry? Why? 2. (3 points) A bandpass filter H.(f) has a frequency response He(f) = } (sinc( 141000)) +sing ( 15+:2000))). 2.a. Calculate the equivalent bandpass filter H; (f). 2.b. The input of the filter is a passband signal xc(t) with in-phase and quadrature components given by xi(t) = 12 cos(6nt) + 3 cos (107) IQ(t) = 2 sin(67t) + 3 sin(10ft) Calculate the Fourier transform of the input signal. 2.c. Calculate the output of the filter in the time domain. 1. (5 points) Consider a passband signal whose in-phase part is a rectangle of unit height and duration 1 second, while the quadrature part is a rectangle of height equal to 2 and duration 2 seconds (both starting from time zero). The carrier frequency is 20 Hz. 1.a. Plot the passband signal in the time domain using MATLAB: Ts=...; %sampling period t=[0:Ts: 100); fc=20; %carrier frequency xi=... ; %in-phase signal xq=... ; %quadrature signal xz=xi+j*xq; %complex envelope xc=sqrt(2) *real(...); %passband signal (you can also use the formula with cosine and sine) tzoom=[0: Ts:3]; %reduced time axis for plotting in the time domain ltzoom=length(tzoom); plot(tzoom, xc(1:ltzoom)); 1.b. Calculate the Fourier transform of the passband signal using MATLAB. N=...; f=...; Xc=...; 1.c. Plot real and imaginary parts of the Fourier transform of the passband signal using MATLAB. 1.d. Using MATLAB, calculate the Fourier transform of the complex enve- lope. 1.e. Plot real and imaginary parts of the Fourier transform of the complex envelope using MATLAB. 1.f. Which of the above Fourier transforms satisfy Hermitian symmetry? Why? 2. (3 points) A bandpass filter H.(f) has a frequency response He(f) = } (sinc( 141000)) +sing ( 15+:2000))). 2.a. Calculate the equivalent bandpass filter H; (f). 2.b. The input of the filter is a passband signal xc(t) with in-phase and quadrature components given by xi(t) = 12 cos(6nt) + 3 cos (107) IQ(t) = 2 sin(67t) + 3 sin(10ft) Calculate the Fourier transform of the input signal. 2.c. Calculate the output of the filter in the time domain
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


