Question: 1. A probability density function is a function f(x ) for which the probability that another quantity X is between a and b is equal
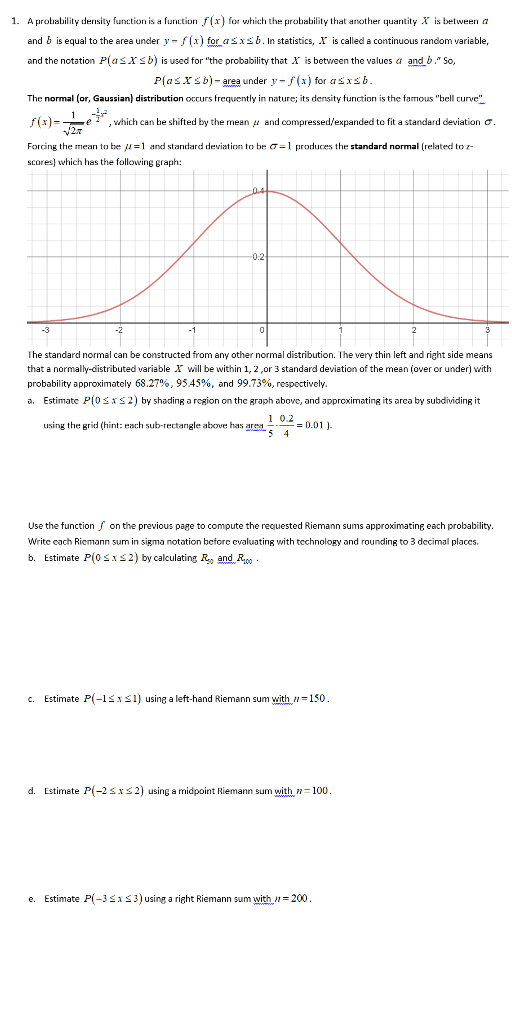


1. A probability density function is a function f(x ) for which the probability that another quantity X" is between a and b is equal to the area under y - / (x) for as x b . In statistics, _\\" is called a continuous random variable, and the notation P(as X's b) is used for "the probability that X" is between the values o and b." So, P(as X sb) - area under y - f(x) for asxsb. The normal (or, Gaussian) distribution occurs frequently in nature; its density function is the famous "bell curve" f(x) = - , which can be shifted by the mean / and compressed/ expanded to fit a standard deviation O . Forcing the mean to be //=1 and standard deviation to be =1 produces the standard normal (related to z- scores) which has the following graph: 0.2 -3 -2 -N -ca The standard normal can be constructed from any other normal distribution. The very thin left and right side means that a normally-distributed variable \\" will be within 1, 2,or 3 standard deviation of the mean (over or under) with probability approximately 68.27%, 95.45%, and 99.73%, respectively. a. Estimate P(0 S * $ 2) by shading a region on the graph above, and approximationg its arca by subdividing it using the grid (hint: each sub-rectangle above has area- 1 0.2 - 5 4 = = 0.01 )- Use the function /' on the previous page to compute the requested Riemann sums approximations each probability. Write each Riemann sum in sigma notation before evaluating with technology and rounding to 3 decimal places. b. Estimate P(0 S x $ 2 ) by calculating Ry and Ryco . c. Estimate P(-15 x $1) using a left-hand Riemann sum with # = 150. d. Estimate P(-2 5 x 2) using a midpoint Riemann sum with # = 100. . Estimate P(-3 5 x $ 3) using a right Riemann sum with " = 200." The probability dentity fur tion of A is given as The mean of A can be calculated bry 7) There are 2 red balls and 3 green bails in a box. If 2 balls are randomly selected from the bo what is the probability of the event that one red ball and one green ball are selected? [A) 1/10 (8) 2/10 (C) 4/10 (D) 6/10 8) Three fair coins are tossed at once, what is the probability of obtaining 2 heads and one (A) X (B) 3/B (C) X (D) % 9) A top-seed tennis player is confident that she has 40%% chance of winning each of the slam tournaments next year. What is the probability that she will win 2 grand slams (A) 0,42 (B) 6 x 0,42 x 0.62 (C) 2 x 0.42 x 0.62 (D) 0.42 x 0.62 10) Random variable X has a Normal (or Gaussian) distribution with a mean of 3, and The probability density function of X is (A) ; =exp (x-3) 2V/27 1 (B) =exp (x-3)2 1 (x-3)2 (C) exp 2V/2n 1 (x-3)2] (D) V2n =expA shuttle bus operates from a shopping centre, travels to Towns A and B sequentially, and then returns to the shopping centre as shown in Figure 2. Shopping Centre Town A Town B Tz Figure 2. Assume that the respective travel times under normal traffic conditions are independent random variables with the following distributions and statistics: Page 3 of 5 CIVL2050 Engineering Computations and Probability WI 2018 Table 1 Travel time Distribution Mean (min) C.O.V Gaussian 30 0.30 T2 Lognormal 20 0.20 Ta Lognormal 40 0.30 However, during rush hours (8:00 - 10:00am and 4:00-6:00pm) the mean travel time between Town A and Town B will increase by 50% with the same c.o.v. Write a Monte Carlo Simulation program using VBA/VB and determine the following probabilities so that the estimates lie within +0.01 of the true value with 95% confidence. a) The scheduled time for one round trip of the shuttle bus is 2 hours. Determine the probability that a round trip will not be completed on schedule under normal traffic conditions. b) What is the probability that a passenger, originating in Town A, will arrive at the shopping centre within 1hr under normal traffic conditions? c) Twice as many passengers originate from Town B than Town A. What Percentage of the passengers will arrive at the shopping centre during rush hours in less than 1hr? d) A passenger starting from Town B has an appointment at 3:00pm at the shopping centre. If the bus left Town B at 2:00pm but has not arrived at the shopping centre at 2:45pm, what is the probability that they will arrive on time for their appointment
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


