Question: 1. A spring has natural length 2? cm. Compare the work (in J] W1 done in stretching the spring from 2? cm to 3? cm

![(in J] W1 done in stretching the spring from 2? cm to](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/666215faa6d7b_186666215fa99342.jpg)

![from 3? cm to 4? cm. {Use kfer the spring constant.) WC]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/666215fb2230e_187666215fb10d0c.jpg)
1.


![x m beyond its natural length is given by x] = 30:,](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/666215fbe6c5c_187666215fbd0cac.jpg)
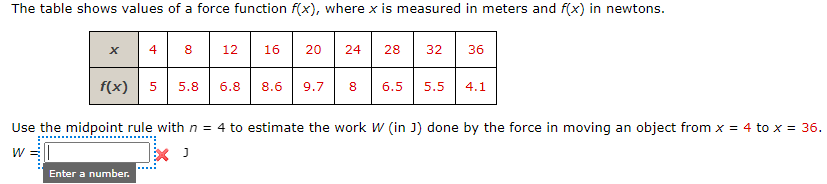
A spring has natural length 2? cm. Compare the work (in J] W1 done in stretching the spring from 2? cm to 3? cm with the work [in J} W2 done in stretching it from 3? cm to 4? cm. {Use kfer the spring constant.) WC] 1 x 2 at How are W2 and W1 related? W2=(|:|X )Wl According to Hooke's LawI the force required to hold the spring stretched x m beyond its natural length is given by x] = 30:, where .i: is the spring constant. Suppose that 6 J of work is needed to stretch a spring from its natural length of 24 cm to a length of 35 cm. Find the exact yalue of k, in Wm. ms): m (a) How much work (in J) is needed to stretch the spring from 29 cm to 33 cm? (Round your answer to two decimal places} :3" {Is} How far beyond its natural length {in cm} will a force of SCI N keep the spring stretched? [Round your answer one decimal place} :3: cm The table shows values of a force function f(x), where x is measured in meters and f(x) in newtons. X 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 f(x) 5 5.8 6.8 8.6 9.7 8 6.5 5.5 4.1 Use the midpoint rule with n = 4 to estimate the work W (in ]) done by the force in moving an object from x = 4 to x = 36. W J Enter a number
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


