Question: Peritoneal dialysis is an alternative method of dialysis in which solute exchange occurs across the peritoneal membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. This approach
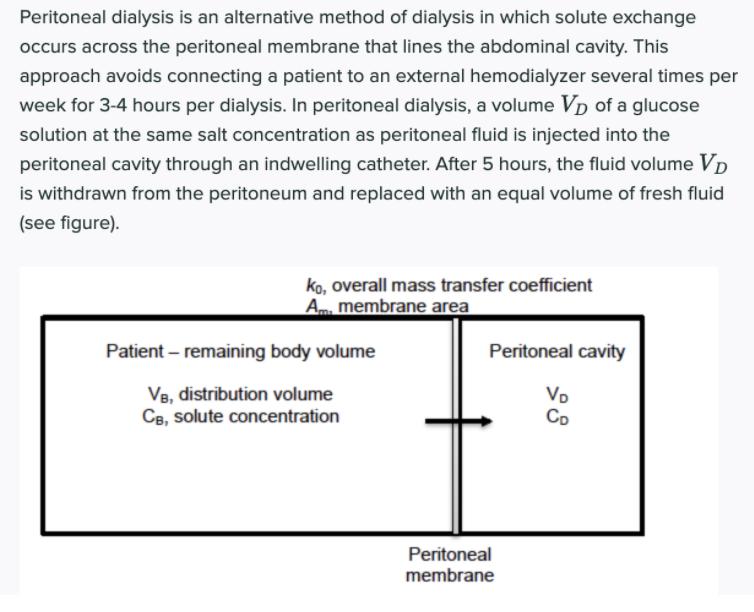

Peritoneal dialysis is an alternative method of dialysis in which solute exchange occurs across the peritoneal membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. This approach avoids connecting a patient to an external hemodialyzer several times per week for 3-4 hours per dialysis. In peritoneal dialysis, a volume Vp of a glucose solution at the same salt concentration as peritoneal fluid is injected into the peritoneal cavity through an indwelling catheter. After 5 hours, the fluid volume Vp is withdrawn from the peritoneum and replaced with an equal volume of fresh fluid (see figure). Ko, overall mass transfer coefficient Am membrane area Patient remaining body volume Peritoneal cavity Vo Co V8, distribution volume CB, solute concentration Peritoneal membrane 1) Based on following data obtained for a 5-hr peritoneal dialysis session, determine the concentration of urea and vitamin B12 at the end of the exchange period as a fraction of the concentration in the body. Please comment based on a clinical point of view- specifically, what should a doctor suggest the dialysis patient do based on your answers? Data: Vp = 2 L; Va = 40 L; KAm = 21 cm' min (Urea) and K.Am = 5 cm' min" (Vitamin B12).
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


