Question: 1. Consider a linear polymer chain with N = 400 Kuhn monomers, with a Kuhn length of b = 4 , in a solvent with
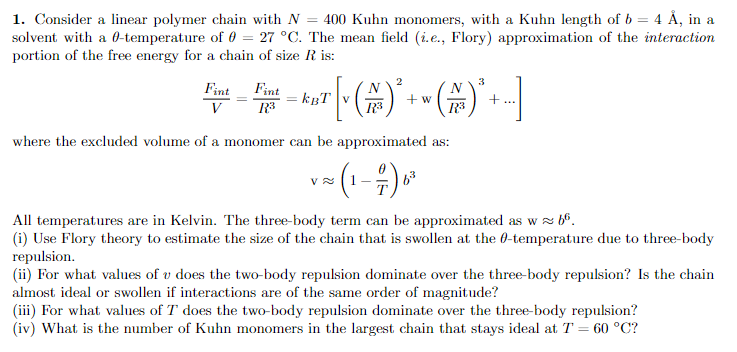
1. Consider a linear polymer chain with N = 400 Kuhn monomers, with a Kuhn length of b = 4 , in a solvent with a 6-temperature of 0 = 27 C. The mean field (i.e., Flory) approximation of the interaction portion of the free energy for a chain of size R is: 2 3 Fint Fint kot [(*+(A)* . w N R3 + V R3 123 where the excluded volume of a monomer can be approximated as: VN - (1-1) 6. All temperatures are in Kelvin. The three-body term can be approximated as w (i) Use Flory theory to estimate the size of the chain that is swollen at the 6-temperature due to three-body repulsion. (i) For what values of v does the two-body repulsion dominate over the three-body repulsion? Is the chain almost ideal or swollen if interactions are of the same order of magnitude? (iii) For what values of T does the two-body repulsion dominate over the three-body repulsion? (iv) What is the number of Kuhn monomers in the largest chain that stays ideal at T = 60 C? 1. Consider a linear polymer chain with N = 400 Kuhn monomers, with a Kuhn length of b = 4 , in a solvent with a 6-temperature of 0 = 27 C. The mean field (i.e., Flory) approximation of the interaction portion of the free energy for a chain of size R is: 2 3 Fint Fint kot [(*+(A)* . w N R3 + V R3 123 where the excluded volume of a monomer can be approximated as: VN - (1-1) 6. All temperatures are in Kelvin. The three-body term can be approximated as w (i) Use Flory theory to estimate the size of the chain that is swollen at the 6-temperature due to three-body repulsion. (i) For what values of v does the two-body repulsion dominate over the three-body repulsion? Is the chain almost ideal or swollen if interactions are of the same order of magnitude? (iii) For what values of T does the two-body repulsion dominate over the three-body repulsion? (iv) What is the number of Kuhn monomers in the largest chain that stays ideal at T = 60 C
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


