Question: 1. Consider a model of diffusion + reaction within a bilayer membrane (see diagram). The membrane consists of two layers, with individual thickness L
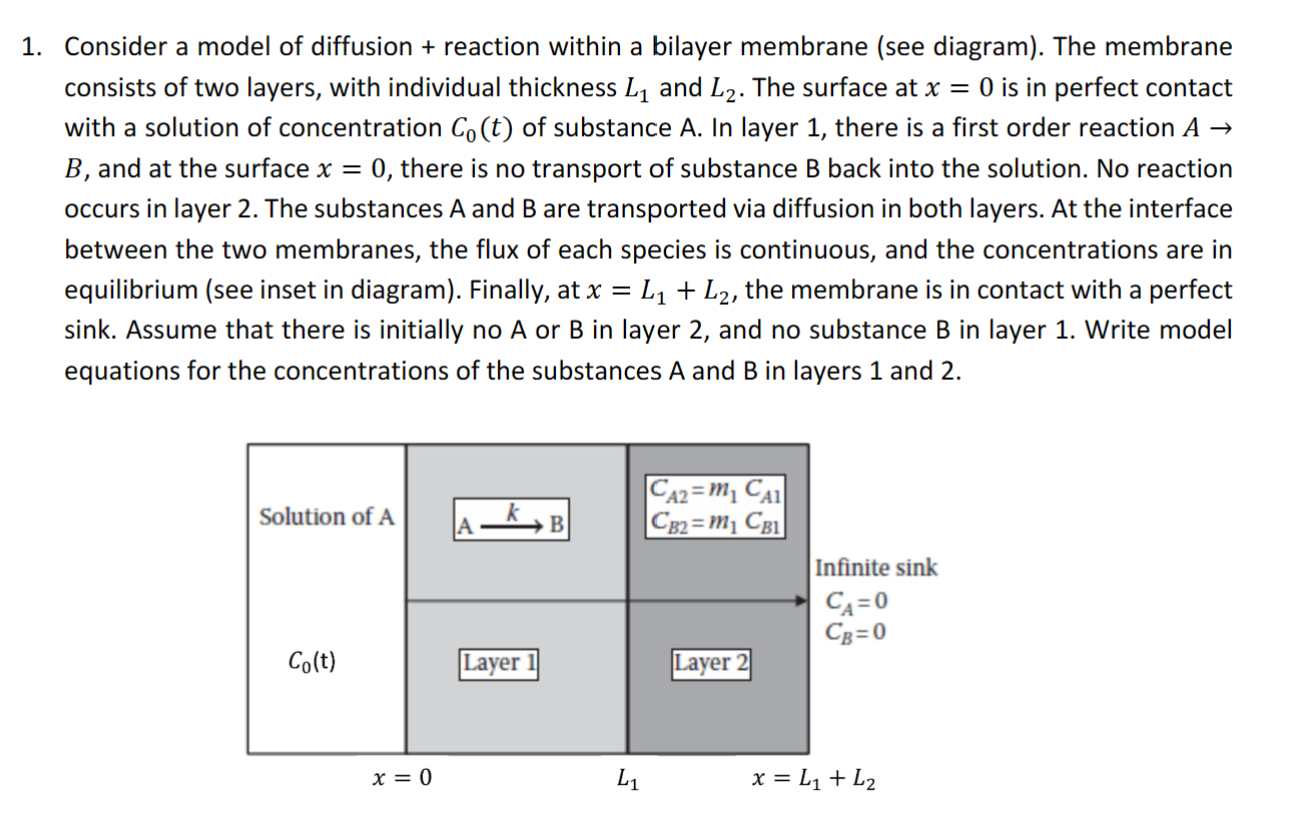
1. Consider a model of diffusion + reaction within a bilayer membrane (see diagram). The membrane consists of two layers, with individual thickness L and L. The surface at x = 0 is in perfect contact with a solution of concentration Co(t) of substance A. In layer 1, there is a first order reaction A B, and at the surface x = 0, there is no transport of substance B back into the solution. No reaction occurs in layer 2. The substances A and B are transported via diffusion in both layers. At the interface between the two membranes, the flux of each species is continuous, and the concentrations are in equilibrium (see inset in diagram). Finally, at x = L + L, the membrane is in contact with a perfect sink. Assume that there is initially no A or B in layer 2, and no substance B in layer 1. Write model equations for the concentrations of the substances A and B in layers 1 and 2. Solution of A Co(t) x = 0 A _k, Layer L CA2=M CA1 CB2=m CB1 Layer 2 Infinite sink CA=0 CB=0 x = L + L
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


