Question: 1. Consider problem of approximationg numerically the definite integral I = Sof(x) dx by an approximation In with n subintervals of width h = (b
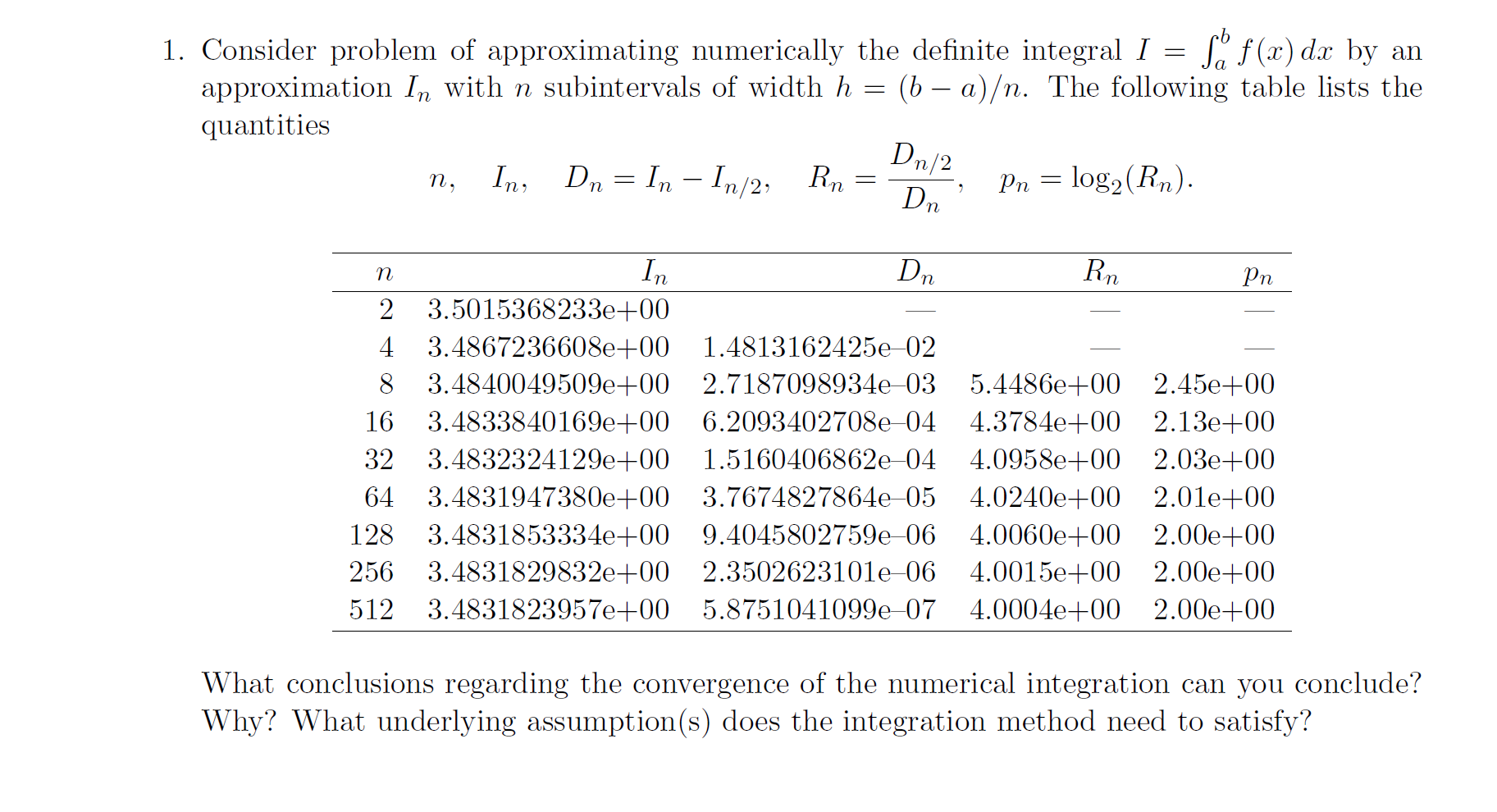
1. Consider problem of approximationg numerically the definite integral I = Sof(x) dx by an approximation In with n subintervals of width h = (b - a). The following table lists the quantities n , In, Dn = In - In/2. Rin = Dn/2 pn = 10g2(Rn). Dn n In Dn Rn Pn 2 3.5015368233e+00 4 3.4867236608e+00 1.4813162425e-02 8 3.4840049509e+00 2.7187098934e 03 5.4486e+00 2.45e+00 16 3.4833840169e+00 6.2093402708e 04 4.3784e+00 2.13e+00 32 3.4832324129e+00 1.5160406862e-04 4.0958e+00 2.03e+00 64 3.4831947380e+00 3.7674827864e-05 4.0240e+00 2.01e+00 128 3.4831853334e+00 9.4045802759e-06 4.0060e+00 2.00e+00 256 3.4831829832e+00 2.3502623101e-06 4.0015e+00 2.00e+00 512 3.4831823957e+00 5.8751041099e-07 4.0004e+00 2.00e+00 What conclusions regarding the convergence of the numerical integration can you conclude? Why? What underlying assumption(s) does the integration method need to satisfy
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


