Question: 1. Consider the graph showing a bicyclist's elevation relative to his elevation above sea level at the start of the race. The first 20 s



![B I]! re 2|} Tin1e{s} Height {m} What do these slopes tell](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6664306784963_023666430676cf76.jpg)
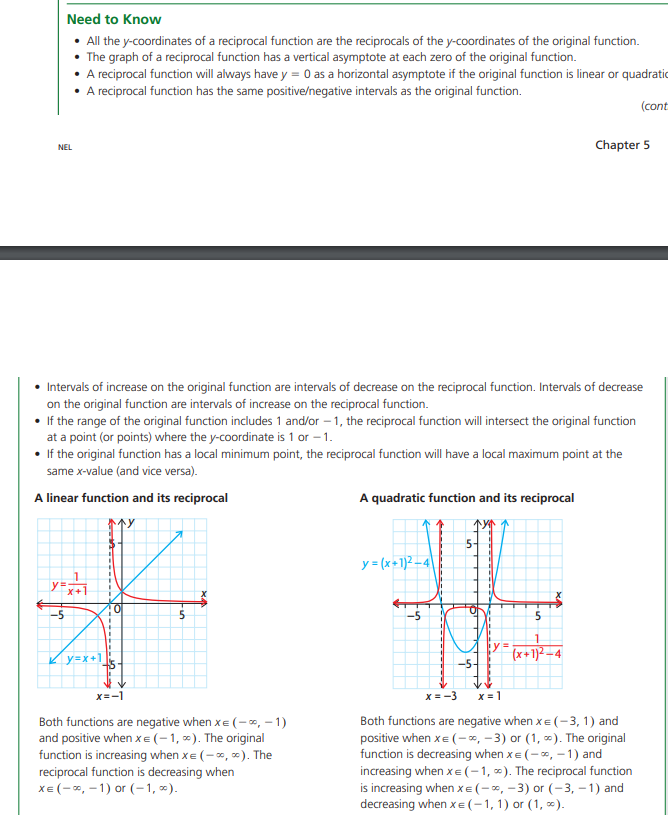
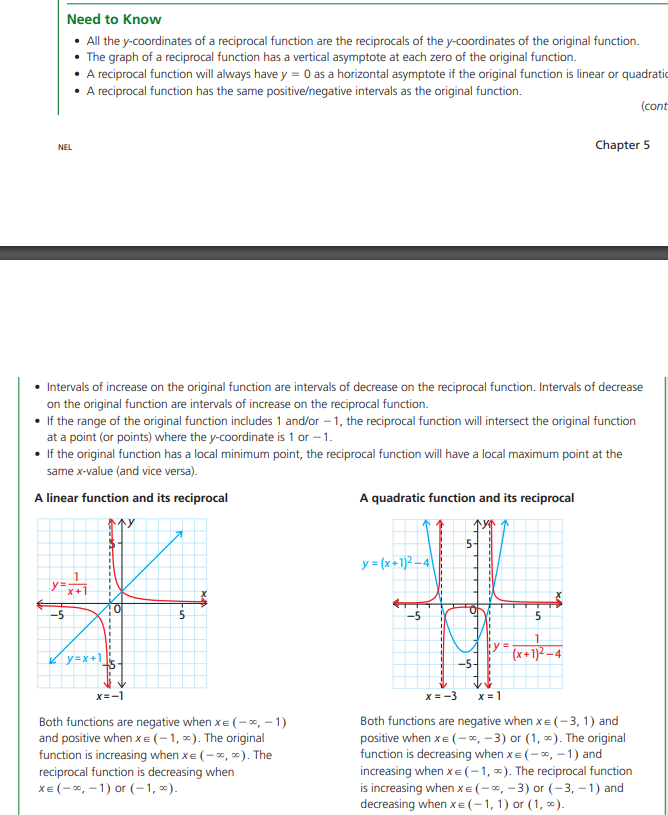
1. Consider the graph showing a bicyclist's elevation relative to his elevation above sea level at the start of the race. The first 20 s of the race are shown. a) On which intervals will the tangent slope be positive? Negative? I: 1' Zero? Ir i.-5Ire- 4 B I]! re 2|} Tin1e{s} Height {m} What do these slopes tell you about the elevation oithe bicyclist? 2. A construction worker drops a bolt while working on a highrise building 32D tn above the ground. Aert seconds, the bolt's height above the ground is 5 meters, where slt) = 320 5t! , ID - I S 3 . a.) Find the average velocity for the interval 3 E t E E. b) Find the bolt's velocity at t= 2 s. 3. The height1 h, in meters of a to}r rocket above the ground can be modeled by the function Fi) 2 5t'2 + 50: , where t represent time in seconds. a) Find the instantaneous speed at t = 4 s. b} Find the instantaneous speed at t= it! s. e) What is the average speed over the interval from t = I} to t = It]? Investigating Reciprocal Functions of the form y = f (x) Is it possible to graph f(x) = - starting with f (x) = x? What do you notice about the two graphs?Need to Know I All the pcoordinates of a reciprocal function are the reciprocals of the y-coordinates of the original function. I The graph of a reciprocal function has a vertical asymptote at each zero of the original function. I A reciprocal function will always have 3* = U as a horizontal asvmptote if the original function is linear or quadratic I A reciprocal function has the same positivahegative intervals as the original function. [cont HEL Chapter 5 I Intervals of increase on the original function are intervals of decrease on the reciprocal function. Intervals of decrease on the original function are intervals of increase on the reciprocal function. I If the range of the original function includes 1 andv'or l, the reciprocal function will intersect the original function at a point {or points] where the Jar-coordinate is 1 or 1. I If the original function has a local minimum point, the reciprocal function will have a local maximum point at the same x-value [and vice versal. A linear function and its reciprocal A quadratic function and its reciprocal J!" Jr: 1 Both functions are negative when x E [ 1r 1 ]: Both functions are negative when x E f 3, 1 1 and and positive when a E ( 1, I}. The original positive when IE fI, 31 or [1, I 1. The original function is increasing when IE { I, I j. The function is decreasing when it E l I, 1 j and reciprocal function is decreasing when increasing when x E [ 1, I 1. The reciprocal function IE { I, 1} or f 1r I}. is increasing whenJrE fI, 3]I or {3, 1'] and decreasing 1.Irrl'renmrEIflr 1} or [1, I}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


