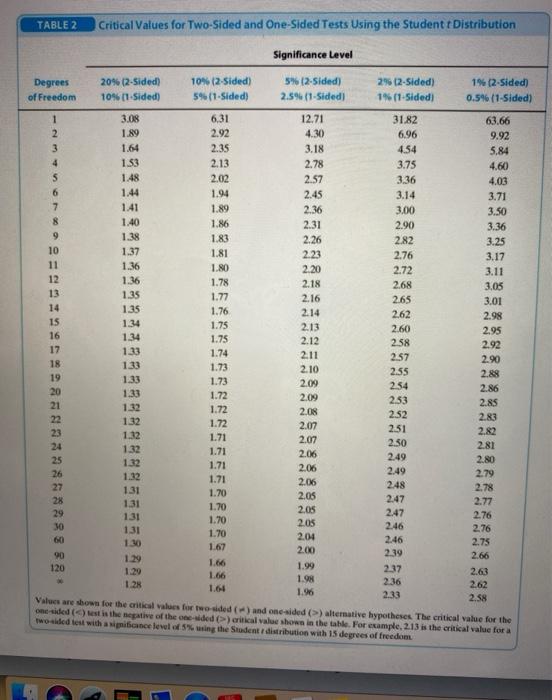
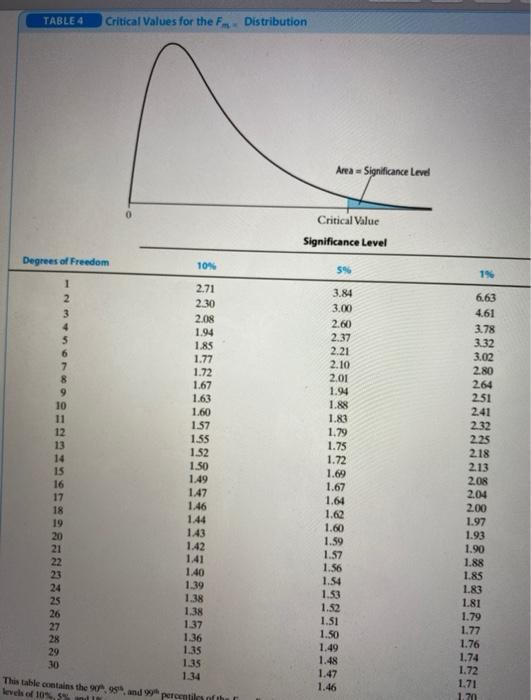
Question: 1. Consider the regression model: In(savi) = Bo + B, In (inct) + uz where In(sav) is the natural log of annual savings of household

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


