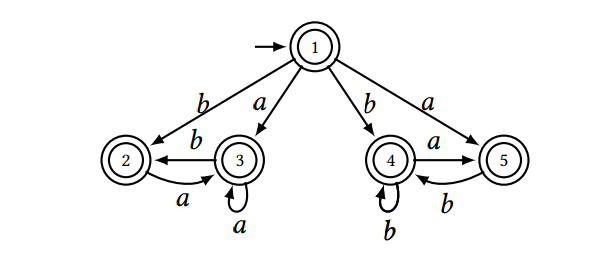
Question: 1. Convert the following NFA into an equivalent DFA. Name each DFA state to indicate which set of NFA states it corresponds to. Also remove
1. Convert the following NFA into an equivalent DFA. Name each DFA state to indicate which set of NFA states it corresponds to. Also remove all unreachable states.
2. Below are two DFAs, M1 and M2. Give a DFA that accepts all strings that are ineither L(M1) or L(M2), but not both.
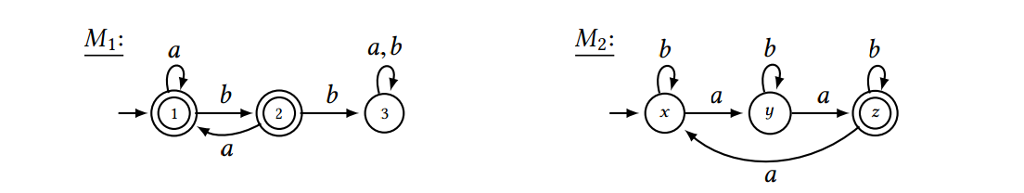
3. An interesting way to think about the guess-and-check nature of nondeterminism is to pretend that the guesses are given as part of the input:
(a) Consider the alphabet = {0,1,0,1}. Draw an NFA for the following language: {w |w contains exactly one character from {0,1}, and w is a binary encoding of a multiple of 3, if you ignore the bars over characters}
(b) Construct an NFA for the following language: {w {0,1} | there is a way to ip exactly 1 bit in w to get a multiple of 3} For example, 1011 should be accepted since ipping the second bit gives 1111, which is a multiple of 3. 1010 should not be accepted, since none of {0010,0110,1000,1011} are a multiple of 3.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


