Question: 1 . Create a fully functional doubly linked list, a linked list object from your class and demonstrate complete testing and full functionality of your
Create a fully functional doubly linked list, a linked list object from your class and demonstrate complete testing and full functionality of your linked list.
There are several files in the starter repo. Only modify the following:
a linkedlist.h: This is your linked list header file.
b linkedlist.cpp: This is your linked list code file.
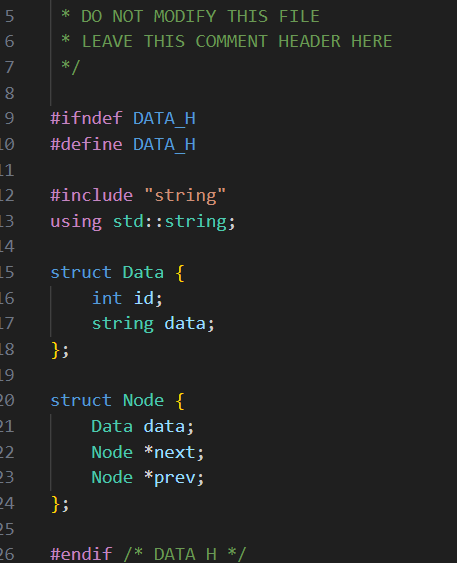
The linked list itself will be a collection of selfreferential nodes defined for you in data.h
Your class will have oneandonlyone class attribute: Node head; a pointer to the first node, or NULL if the list is empty.
Upon creation, the linkedList object will be empty ie It will contain no nodes. head will point to NULL or nullpointer. Upon destruction, call your clearList method.
Methods may not be more than about lines long. If they are, break them up into properly modular methods. You may make any private methods you like.
Public methods these are the only public methods allowed:
a bool addNodeint string; pass this method an int id and some nonempty string by reference. The id must be unique and a positive number greater than Return true or false to indicate success or failure. Nodes added must be stored in ascending order of id Memory for the node must be allocated inside the linked list object. This method must do proper error checking. Ids cannot be negative and duplicate ids are not allowed. The test code will test this. DO NOT use your own exists method to look for nonunique ids, and do not duplicate the exists functionality to look for nonunique ids.
i You want to first only verify your id is a positive int, and the string is nonempty, then search for the place to add the new node, and during the search look for duplicates, then after you determine there is no duplicate, then allocate your memory and insert the node. This is the algorithm you must follow
b bool deleteNodeint; pass this method an id to delete. Return true or false to indicate success or failure. Delete the memory the node was using. DO NOT use your own exists method or anything like exists to first look for the id to delete, just search and delete in one loop.
c bool getNodeint Data; pass this method an id and an empty struct Data passed by reference from main If the id is found, fill the empty struct Data passed by reference, and return true. If the id is not found, place a in the id and empty string in the string and return false. DO NOT use your own exists method or anything like exists to look first for the node, just search and find it in one loop.
d void printListbool false; Will print out the entire list in order, either forward or backward, based on the bool passed in Make the bool default to false ie forward Your prototype will look as given, and your definition should be something like void printListbool backward This is the only method allowed to print.
e int getCount; Get a count of the nodes in the list. You must calculate count on the fly each time this is called. You may not maintain a class attribute count. f bool clearList; Resets the linked list, deletes all allocated memory and sets head NULL;
g bool existsint; Checks to see if an id exists in the list. Adding and deleting always leaves the link list properly sorted in ascending order.
Remember all good programming objectoriented and procedural programming practices including but not limited to the following:
a Use loose coupling
b Only one return per statement.
c Do not repeat yourself. The most common place people break this rule is in allocating a new node and assigning values to that node. Do not duplicate any code, especially node allocationassignment code.
d Never use break or continue in loops.
e Keep functions small, no more than about two dozen lines.
f Do not nest if statements or loops more than deep.
All testing is written for you in main. Do not modify the tests or any other files.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


