Question: 1. Current Stage Previous Stage Non-REM Previous Stage REM Previous Stage Wake Non-REM 32445 136 1692 REM 351 7584 182 Wake 1675 380 6956 Totals
1.
| Current Stage | Previous Stage Non-REM | Previous Stage REM | Previous Stage Wake |
| Non-REM | 32445 | 136 | 1692 |
| REM | 351 | 7584 | 182 |
| Wake | 1675 | 380 | 6956 |
| Totals | 34471 | 8100 | 8830 |


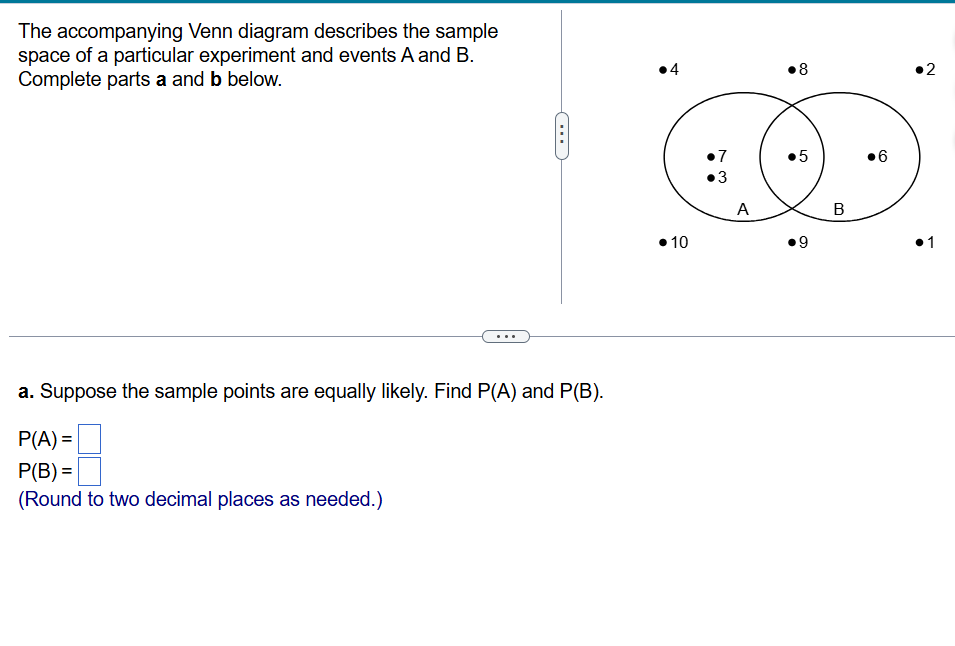

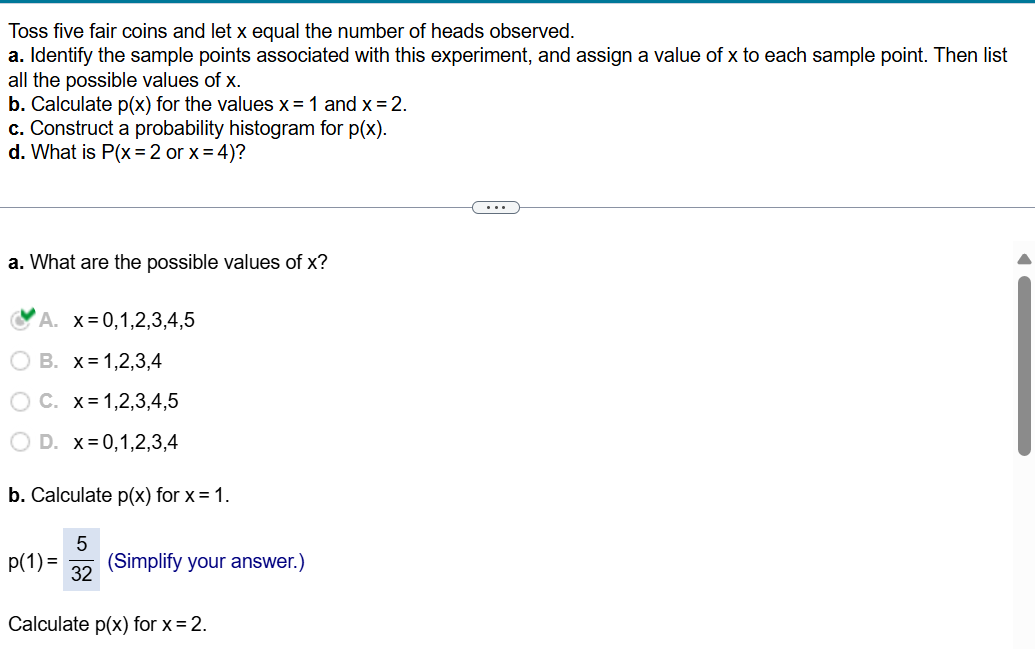
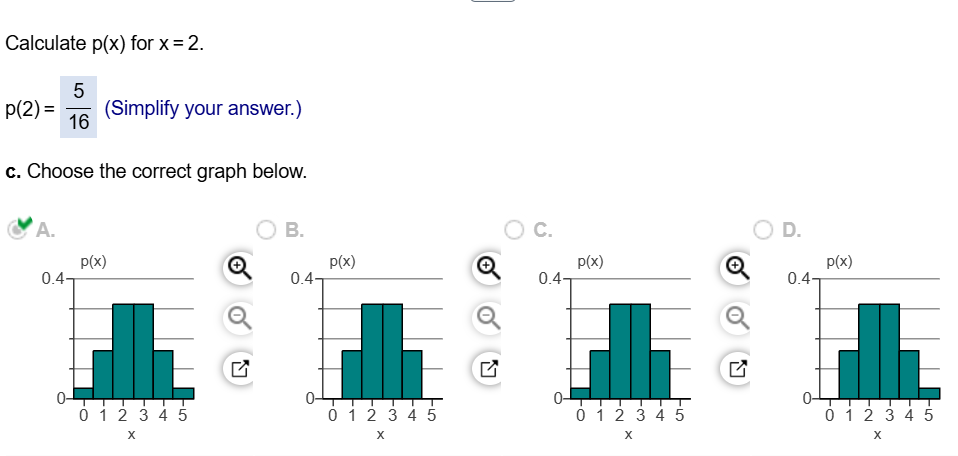
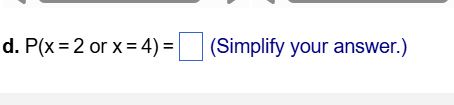
In a study, the various stages of sleep for a large group of people were monitored in 30-second intervals, or "epochs.\" For each epoch, sleep stage was categorized as Wake, REM, or Non-REM. The accompanying table provides a summary of the results. Each cell of the table gives the number of epochs that occurred when transitioning from the previous sleep stage to the current sleep stage. Complete parts a through e below. a. Given that the previous sleep stage for the epoch was the REM state, what is the probability that the current sleep stage is REM? The probability is | | (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to three decimal places as needed.) The accompanying Venn diagram describes the sample space of a particular experiment and events A and B. 4 g 5 Complete parts a and b below. g " B 10 9 o1 a. Suppose the sample points are equally likely. Find P(A) and P(B). PA)=| | PB)=| | (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The outcomes of two variables are (Low, Medium, High) and (On, Off), respectively. An experiment is conducted in which the outcomes of each of the two variables are observed. The probabilities associated with each of the six possible outcome pairs are given in the accompanying two-way table. Consider the events below. Complete parts a through h. A: {Low} B: {Low or On} C: {Off and Medium} D: {High} a. Find P(A). P(A)=| | (Type an exact answer in simplified form.) Low Medium High On Off 051 025 0.09 0.05 0.06 0.04 Toss five fair coins and let x equal the number of heads observed. a. Identify the sample points associated with this experiment, and assign a value of x to each sample point. Then list all the possible values of x. b. Calculate p(x) for the values x=1 and x=2. c. Construct a probability histogram for p(x). d. What is P(x=2 or x=4)? a. What are the possible values of x? x=0,1,2345 x=1,234 x=1,2,3,45 x=0,1,2,3,4 b. Calculate p(x) for x=1. 5 p(1)= 3 (Simplify your answer.) Calculate p(x) for x = 2. \f\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


