Question: 1. Decision analysis will not solve a decision problem, nor is it intended to. Its purpose is to produce insight and promote creativity to help
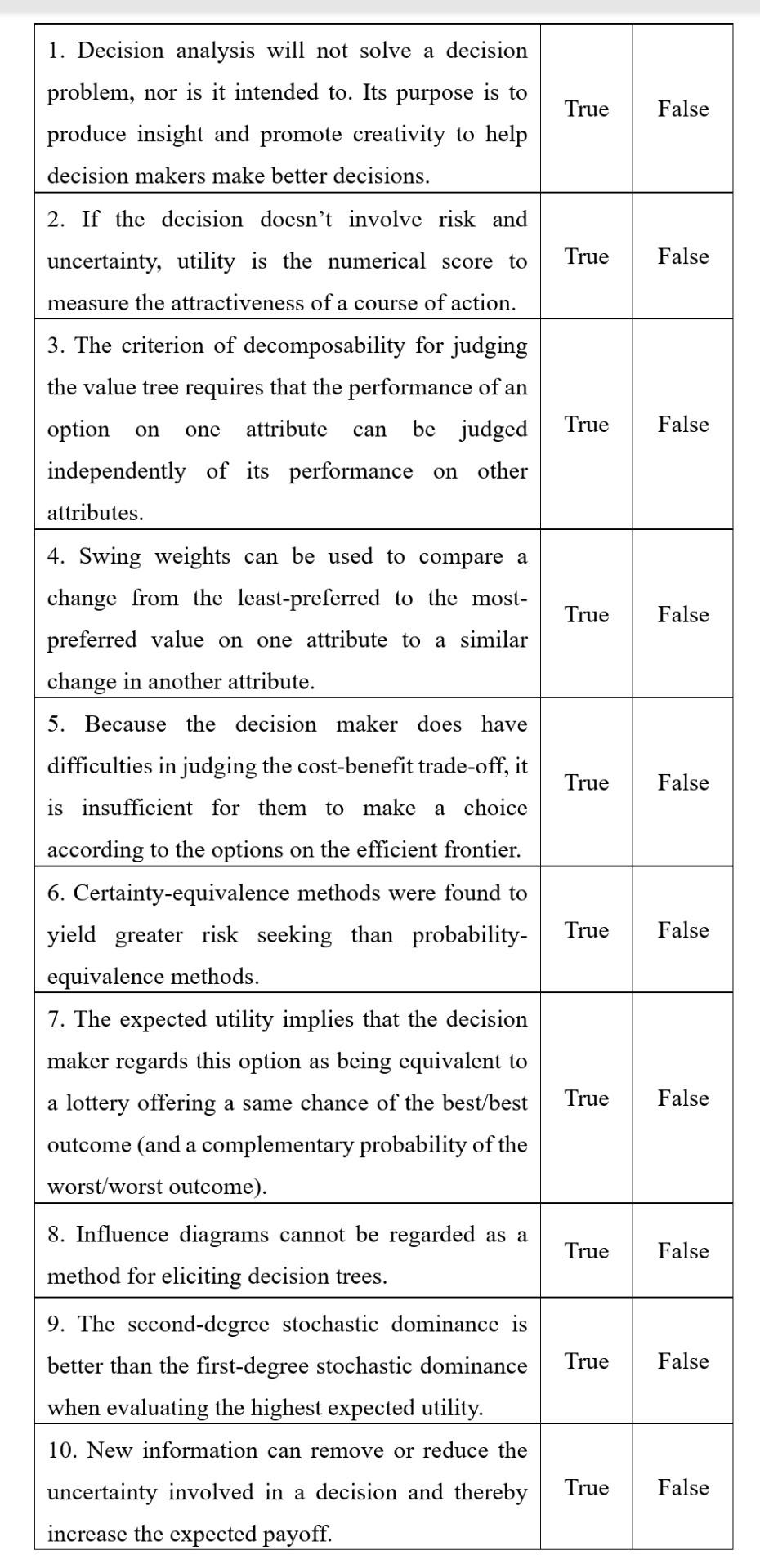
1. Decision analysis will not solve a decision problem, nor is it intended to. Its purpose is to produce insight and promote creativity to help decision makers make better decisions. True False 2. If the decision doesn't involve risk and uncertainty, utility is the numerical score to True False measure the attractiveness of a course of action. 3. The criterion of decomposability for judging the value tree requires that the performance of an option attribute be judged independently of its performance on other attributes. True False one on can 4. Swing weights can be used to compare a change from the least-preferred to the most- preferred value on one attribute to a similar change in another attribute. True False 5. Because the decision maker does have True False True False difficulties in judging the cost-benefit trade-off, it is insufficient for them to make a choice according to the options on the efficient frontier. 6. Certainty-equivalence methods were found to yield greater risk seeking than probability- equivalence methods. 7. The expected utility implies that the decision maker regards this option as being equivalent to a lottery offering a same chance of the best/best outcome (and a complementary probability of the worst/worst outcome). True False True False True False 8. Influence diagrams cannot be regarded as a method for eliciting decision trees. 9. The second-degree stochastic dominance is better than the first-degree stochastic dominance when evaluating the highest expected utility. 10. New information can remove or reduce the uncertainty involved in a decision and thereby increase the expected payoff. True False
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


