Question: 1. Decision making is a process. Support your answer with an example. please use the attached pictures, add references too with the answer Information, rechnology,
1. Decision making is a process. Support your answer with an example.
please use the attached pictures, add references too with the answer
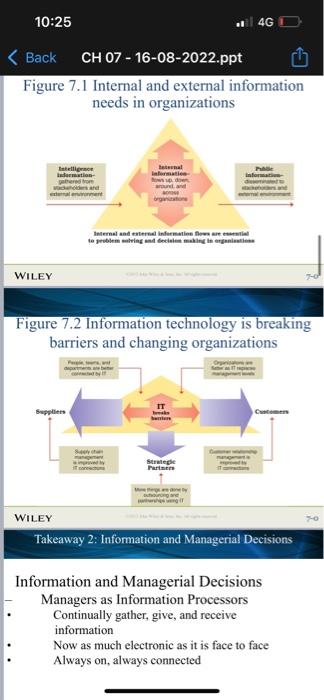
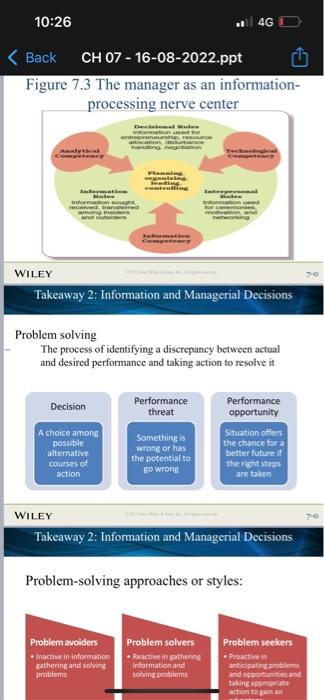
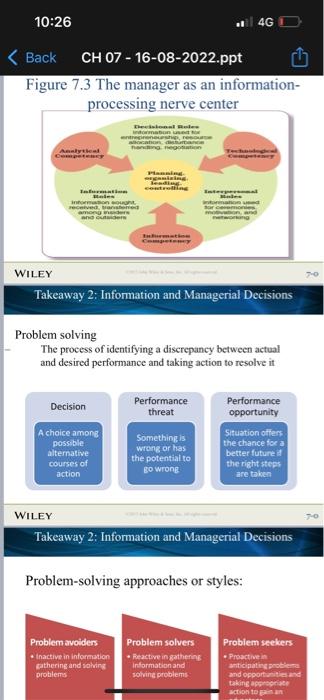
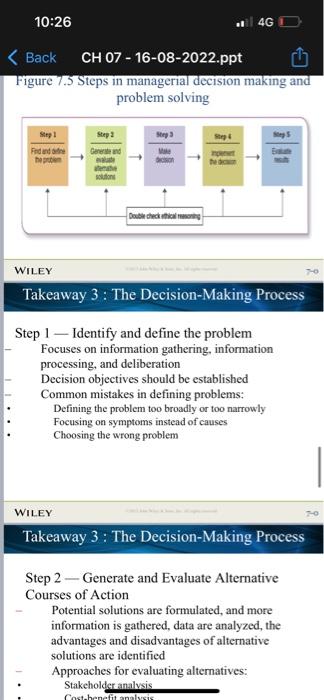
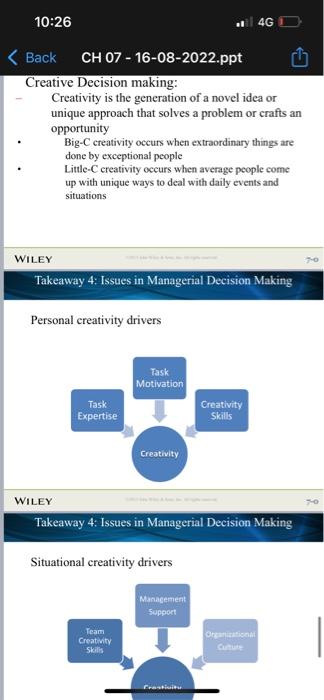
Information, rechnology, and Management What is useful information? Information systems and business intelligence Information needs in organizations How information iechnology is changing organizations Information and Managerial Decisions Managers as infocaution processors Managers as problem solvers Types of managcrial decistons Dccision conditions WILEY Chapter 7 Learning Dashboard WILEY Takeaway 1: Information, Technology, \& Management Information, Technology, \& Management Managers must have Technological competency Ability to understand ncw fechnologics and to use than to their best advantage Information competency Absisy to locate, gather, organize, and display information for decision making and problem solving Analytical competency Ability to evaluate and analyze information to enake actual What is useful information? Data Raw facts and observations Information Data made useful and meaningful for decision making Information drives management functions WILEY Takeaway 1: Information, Technology, \& Management Characteristics of useful information: Timely High quality Complete Relevant Understandable Analytics: systematic gathering and processing of data to make it useful as information WILEY Takeaway 1: Information, Technology, \& Management Information systems and business intelligence Management information systems Use II to collect, organize, and distribute data for use in decision making Business intelligence Taps information systems to extract and report data in organized ways that are helpful to decision makers Executive dashboards Visually update and display key performance indicators and information on a real-time basis WILEY Takeaway 1: Information. Technology, \& Management Information needs in organizations Information exchanges with the external environment: Gather intelligence information Provide public information Information exchanges within the onganization: Facilitate decision making Facilitate problem solving WILEY Takeaway 1: Information, Technology, \& Management Figure 7.1 Internal and external information needs in organizations Figure 7.2 Information technology is breaking barriers and changing organizations Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Information and Managerial Decisions Managers as Information Processors Continually gather, give, and receive information Now as much electronic as it is face to face Always on, always connected Figure 7.3 The manager as an informationprocessing nerve center WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Problem solving The process of identifying a discrepancy between actual and desired performance and taking action to resolve it WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Problem-solving approaches or styles: Systematic versus intuitive thinking WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Multidimensional thinking applies both intuitive and systematic thinking Effective multidimensional thinking requires skill at strategic opportunism WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Managers use different cognitive styles Types of problems Structured problems are ones that are familiar, straightforward, and clear with respect to information needs Programmed decisions apply solutions that are readily available from past experiences to solve structured problems WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Types of problems Unstructured problems are ones that are full of ambiguities and information deficiencies Nonprogrammed decisions apply a specific solution to meet the demands of a unique problem Commonly faced by higher-level management WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Crisis decision making A crisis involves an unexpected problem that can lead to disaster if not resolved quickly and appropriately Figure 7.3 The manager as an informationprocessing nerve center WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Problem solving The process of identifying a discrepancy between actual and desired performance and taking action to resolve it WILEY Takeaway 2: Information and Managerial Decisions Problem-solving approaches or styles: Figure 7.5 Steps in managerial decision making and problem solving WILEY Takeaway 3 : The Decision-Making Process Step 1 - Identify and define the problem Focuses on information gathering, information processing, and deliberation Decision objectives should be established Common mistakes in defining problems: Defining the problem too broadly or too narrowly Focusing on symptoms instead of causes Choosing the wrong problem WILEY Takeaway 3: The Decision-Making Process Step 2 - Generate and Evaluate Alternative Courses of Action Potential solutions are formulated, and more information is gathered, data are analyzed, the advantages and disadvantages of alternative solutions are identified Approaches for evaluating alternatives: Stakeholder analvsis Step 2 - Generate and Evaluate Possible Courses of Action (cont.) Criteria for evaluating alternatives: Benefits Costs Timeliness Acceptability Ethical soundness WILEY Takeaway 3 : The Decision-Making Process Step 2 - Generate and Evaluate Possible Courses of Action (cont.) Common mistakes: Abandoning the search for alternatives too quickly WILEY Takeaway 3 : The Decision-Making Process Step 3 - Decide on a Preferred Course of Action Two different approaches Behavioral model leads to satisficing decisions Classical model leads to optimizing decisions Figure 7.6 Differences in the classical and behavioral decision-making models WILEY Takeaway 3 : The Decision-Making Process Step 4 - Implement the Decision Involves taking action to make sure the solution decided upon becomes a reality Managers need to have willingness and ability to implement action plans Lack-of-participation error should be avoided WILEY Takeaway 3 : The Decision-Making Process Step 5 - Evaluate Results Involves comparing actual and desired results Positive and negative consequences of chosen course of action should be examined If actual results fall short of desired results, the manager returns to earlier steps in the decisionmaking process At all stens check ethical reasoninot WILEY Takeaway 4: Issues in Managerial Decision Making Issues in decision making How do decision errors happen? Heuristics are strategies for simplifying decision making Creative Decision making: Creativity is the generation of a novel idea or unique approach that solves a problem or crafts an opportunity Big-C creativity occurs when extraordinary things are done by exceptional people Little-C ereativity occurs when average people come up with unique ways to deal with daily events and situations WILEY Takeaway 4: Issues in Managerial Decision Making Personal creativity drivers WILEY Takeaway 4: Issues in Managerial Decision Making Situational creativity drivers