Question: 1. Develop a code to find all Nash equilibria in pure strategies for a normal form game of two players with given utility matrixes. Sets
 1. Develop a code to find all Nash equilibria in pure strategies for a normal form game of two players with given utility matrixes. Sets of strategies for all players are finite.
1. Develop a code to find all Nash equilibria in pure strategies for a normal form game of two players with given utility matrixes. Sets of strategies for all players are finite.
2. Develop a code to construct utility matrixes for the game a normal form game of two players when transportation graph is given and population at each node and set of possible spots for cities are given. Assume that customers will go to the closest shop and divide in equal proportion if the distances are the same. Find Nash equilibrium by the code from task 1.
3. Chose and download data of real transportation network, create an object network for it in Python. Find Nash equilibrium by the code from task 1 and 2.
4. Develop a code to apply rationalization method of reduction strategies sets in pure strategies for a normal form game of two players with given utility matrixes. Sets of strategies for all players are finite.
5. Develop a code to apply minmax equilibria in pure strategies for a normal form game of two players with given utility matrixes. Sets of strategies for all players are finite.
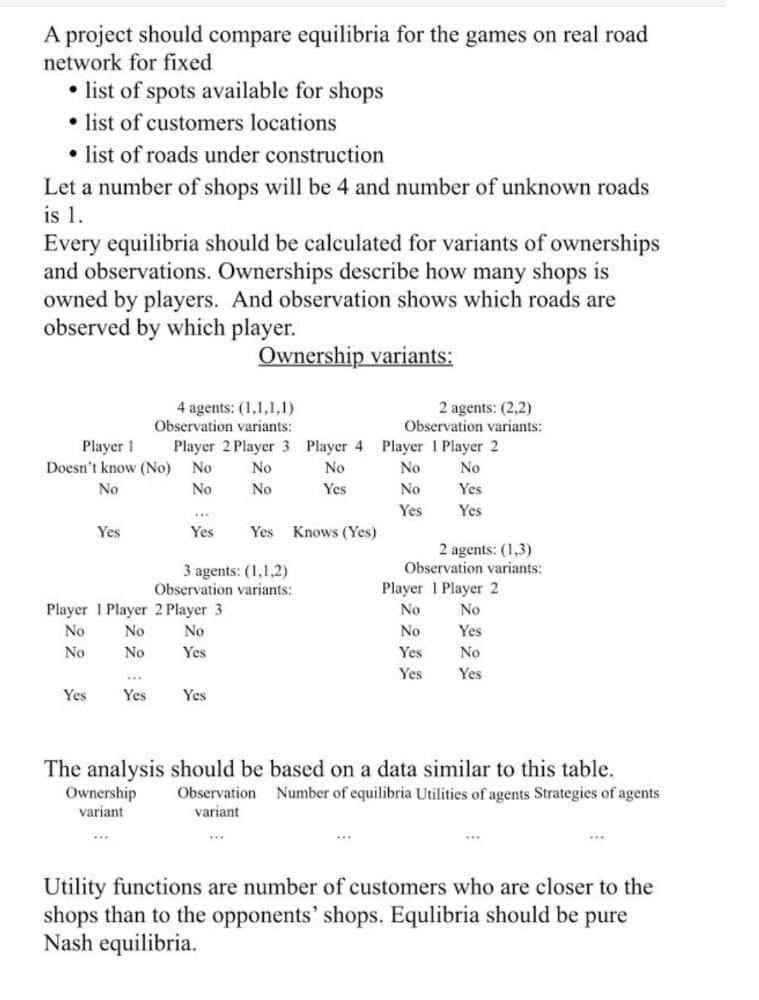
A project should compare equilibria for the games on real road network for fixed list of spots available for shops list of customers locations list of roads under construction Let a number of shops will be 4 and number of unknown roads is 1. Every equilibria should be calculated for variants of ownerships and observations. Ownerships describe how many shops is owned by players. And observation shows which roads are observed by which player. Ownership variants: 4 agents: (1,1,1,1) 2 agents: (2,2) Observation variants: Observation variants: Player 1 Player 2 Player 3 Player 4 Player 1 Player 2 Doesn't know (No) No No No No No No No No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Knows (Yes) 2 agents: (1,3) 3 agents: (1,1,2) Observation variants: Observation variants: Player 1 Player 2 Player 1 Player 2 Player 3 No No No No No No Yes No No Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes The analysis should be based on a data similar to this table. Ownership Observation Number of equilibria Utilities of agents Strategies of agents variant variant Utility functions are number of customers who are closer to the shops than to the opponents' shops. Equlibria should be pure Nash equilibria. A project should compare equilibria for the games on real road network for fixed list of spots available for shops list of customers locations list of roads under construction Let a number of shops will be 4 and number of unknown roads is 1. Every equilibria should be calculated for variants of ownerships and observations. Ownerships describe how many shops is owned by players. And observation shows which roads are observed by which player. Ownership variants: 4 agents: (1,1,1,1) 2 agents: (2,2) Observation variants: Observation variants: Player 1 Player 2 Player 3 Player 4 Player 1 Player 2 Doesn't know (No) No No No No No No No No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Knows (Yes) 2 agents: (1,3) 3 agents: (1,1,2) Observation variants: Observation variants: Player 1 Player 2 Player 1 Player 2 Player 3 No No No No No No Yes No No Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes The analysis should be based on a data similar to this table. Ownership Observation Number of equilibria Utilities of agents Strategies of agents variant variant Utility functions are number of customers who are closer to the shops than to the opponents' shops. Equlibria should be pure Nash equilibria
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


